Textbook Question
Which type (or types) of crystalline solid is characterized by each of the following? (d) network of covalent bonds.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
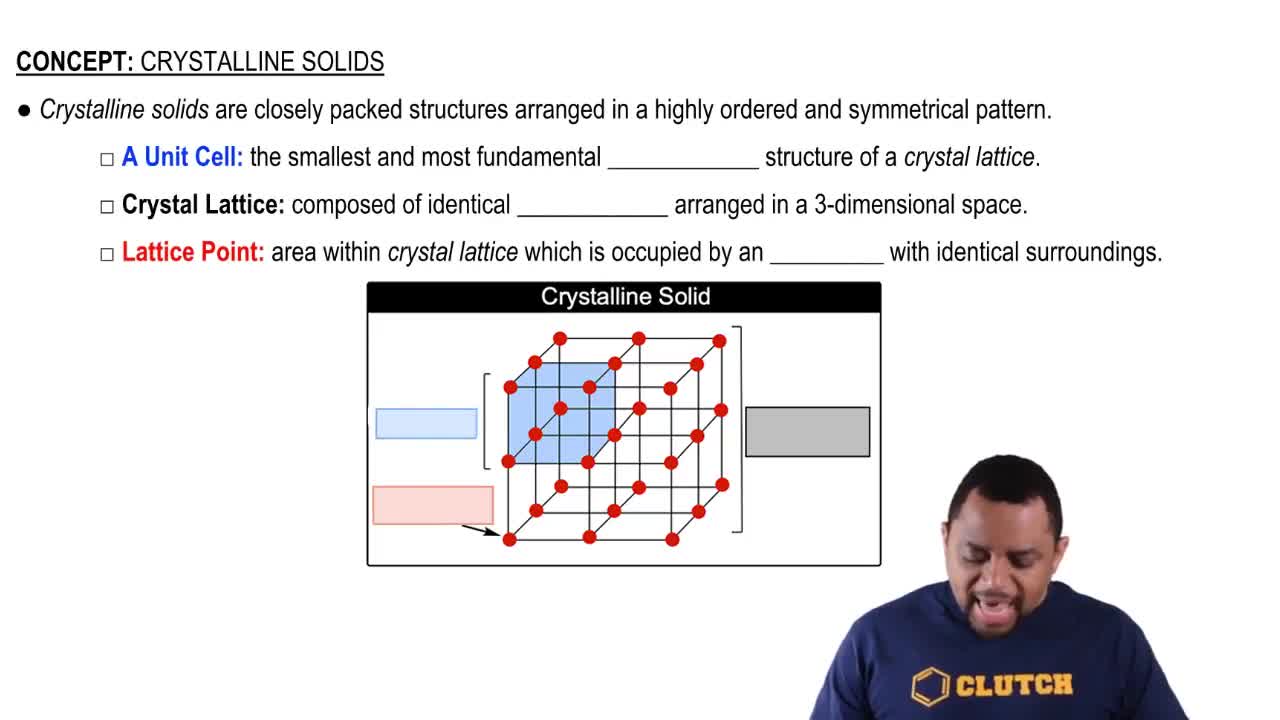
Which type (or types) of crystalline solid is characterized by each of the following? (d) network of covalent bonds.
Which type (or types) of crystalline solid is characterized by each of the following? (c) high melting point and poor electrical conductivity;
Indicate the type of solid (molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network) for each compound: (c) Ta2O5 (melting point, 1872°C)
(a) Draw a picture that represents a crystalline solid at the atomic level.
(b) Now draw a picture that represents an amorphous solid at the atomic level.