Textbook Question
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (b) What wavelength of light would a photon of this energy correspond to?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance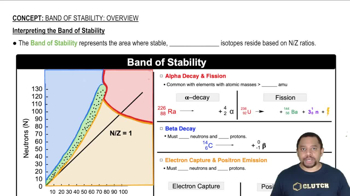
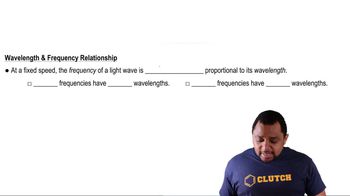
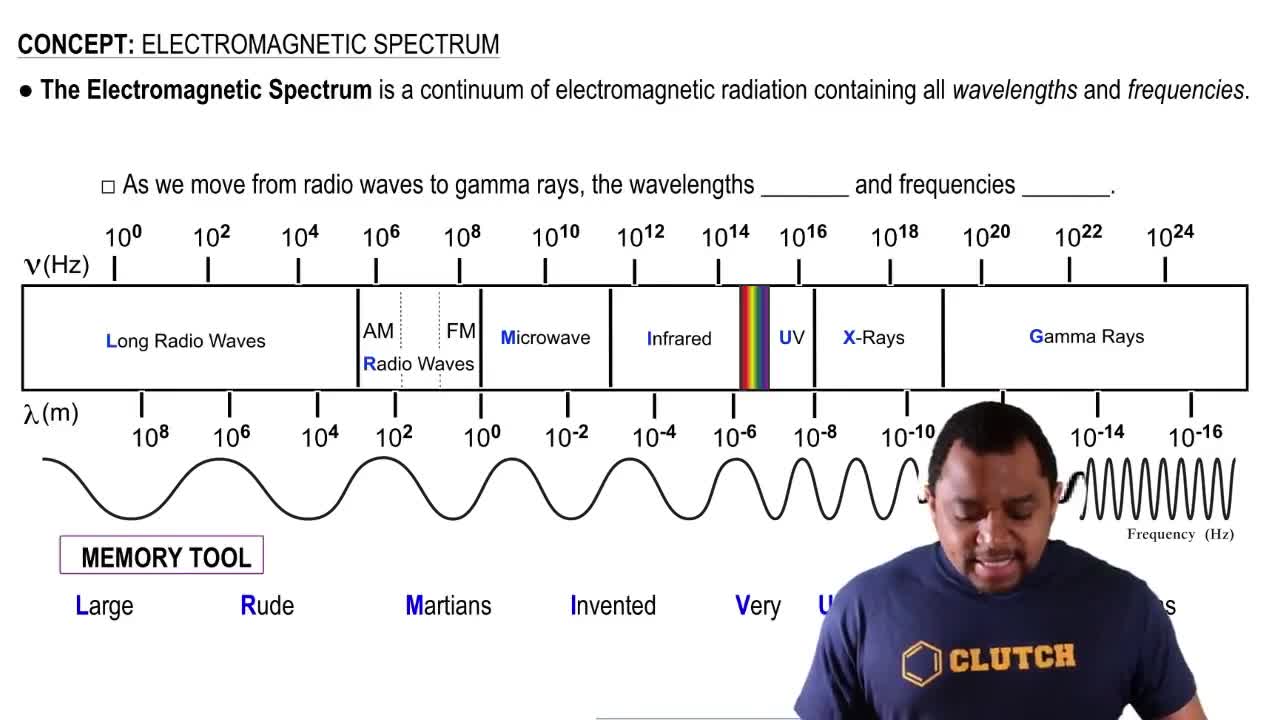
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (b) What wavelength of light would a photon of this energy correspond to?
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (d) With respect to silicon, does CdTe absorb a larger or smaller portion of the solar spectrum?
(a) What is a monomer? (b) Which of these molecules can be used as a monomer: ethanol, ethene (also called ethylene), methane?