Textbook Question
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (d) With respect to silicon, does CdTe absorb a larger or smaller portion of the solar spectrum?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
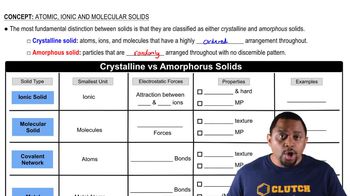
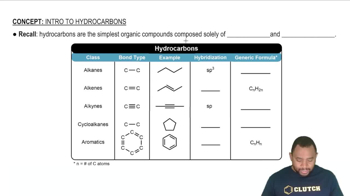
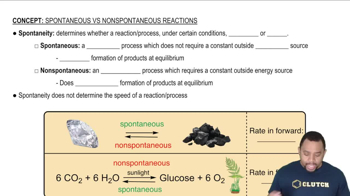
Cadmium telluride is an important material for solar cells. (d) With respect to silicon, does CdTe absorb a larger or smaller portion of the solar spectrum?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the formation of a polymer via a condensation reaction from the monomers succinic acid 1HOOCCH2CH2COOH2 and ethylenediamine 1H2NCH2CH2NH22.