The coordination number for the Al3+ ion is typically between four and six. Use the anion coordination number to determine the Al3 + coordination number in the following compounds: (b) Al2O3 where the oxygen ions are six coordinate.

Classify each of the following statements as true or false: (a) For molecular solids, the melting point generally increases as the strengths of the covalent bonds increase. (b) For molecular solids, the melting point generally increases as the strengths of the intermolecular forces increase.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Molecular Solids
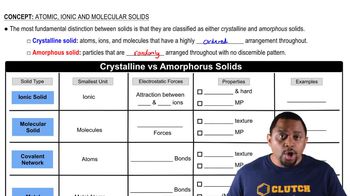
Intermolecular Forces
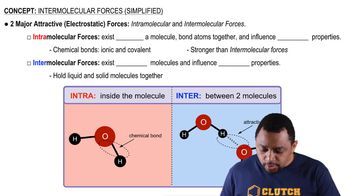
Covalent Bonds vs. Intermolecular Forces

The coordination number for the Al3+ ion is typically between four and six. Use the anion coordination number to determine the Al3 + coordination number in the following compounds: (c) AlN where the nitride ions are four coordinate.
Both covalent-network solids and ionic solids can have melting points well in excess of room temperature, and both can be poor conductors of electricity in their pure form. However, in other ways their properties are quite different. (a) Which type of solid is more likely to dissolve in water?
For each of the following pairs of semiconductors, which one will have the larger band gap: (a) CdS or CdTe? (b) GaN or InP? (c) GaAs or InAs?
If you want to dope GaAs to make an n-type semiconductor with an element to replace Ga, which element would you pick? a. Zn b. Al c. In or d. Si
