Based on the type or types of intermolecular forces, predict the substance in each pair that has the higher boiling point: (a) propane (C3H8) or n-butane (C4H10) (b) diethyl ether (CH3CH2OCH2CH3) or 1-butanol (CH3CH2CH2CH2OH) (c) sulfur dioxide (SO2) or sulfur trioxide (SO3) (d) phosgene (Cl2CO) or formaldehyde (H2CO)
Ch.11 - Liquids and Intermolecular Forces

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 11, Problem 34
The generic structural formula for a 1-alkyl-3-methylimid- azolium cation is where R is a -CH2(CH2)nCH3 alkyl group. The melting points of the salts that form between 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cation and the PF6- anion are as follows: R = CH2CH3 (m.p. = 60 °C), R = CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = 40 °C), r = CH2CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = 10 °C), and R = CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 (m.p. = -61 °C). Why does the melting point decrease as the length of alkyl group increases?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the trend in melting points as the alkyl chain length increases: the melting point decreases.
Understand that the melting point is influenced by the strength of intermolecular forces in the solid state.
Recognize that longer alkyl chains increase the hydrophobic character and disrupt the packing efficiency of the ions in the solid state.
Explain that as the alkyl chain length increases, the van der Waals forces become more significant, but the overall packing becomes less efficient, leading to a decrease in melting point.
Conclude that the decrease in melting point with increasing alkyl chain length is due to the reduced packing efficiency and increased disorder in the solid state.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces are the attractive forces between molecules that influence physical properties such as melting and boiling points. In ionic compounds, like the salts formed from 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium cations and PF6- anions, the strength of these forces is crucial. As the alkyl chain length increases, the overall molecular size increases, which can lead to weaker interactions due to increased distance between charged regions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
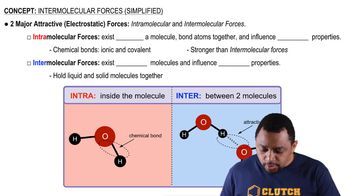
Intermolecular vs Intramolecular Forces
Hydrophobic Effect
The hydrophobic effect refers to the tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in aqueous solutions to minimize their exposure to water. In the context of ionic liquids, longer alkyl chains are more hydrophobic, which can disrupt the packing of ions in the solid state. This disruption can lead to a decrease in the melting point as the solid structure becomes less stable with longer, bulkier alkyl groups.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Photoelectric Effect
Crystal Lattice Energy
Crystal lattice energy is the energy released when ions in the gas phase come together to form a solid ionic compound. It is a measure of the stability of the ionic lattice. As the alkyl chain length increases, the lattice energy may decrease due to the larger size and lower charge density of the cation, resulting in weaker ionic interactions and a lower melting point for the resulting salts.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lattice Energy
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A number of salts containing the tetrahedral polyatomic anion, BF4-, are ionic liquids, whereas salts containing the somewhat larger tetrahedral ion SO42- do not form ionic liquids. Explain this observation.
Textbook Question
(b) What is the relationship between viscosity and temperature?
Textbook Question
(c) Why do substances with high surface tension also tend to have high viscosities?
Textbook Question
Based on their composition and structure, list CH2Cl2, CH3CH2CH3, and CH3CH2OH in order of (a) increasing intermolecular forces (c) increasing surface tension
