Based on their composition and structure, list CH2Cl2, CH3CH2CH3, and CH3CH2OH in order of (a) increasing intermolecular forces (c) increasing surface tension

Name the phase transition in each of the following situations and indicate whether it is exothermic or endothermic: (a) When ice is heated, it turns to water. (b) Wet clothes dry on a warm summer day. (c) Frost appears on a window on a cold winter day. (d) Droplets of water appear on a cold glass of lemonade.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Phase Transitions
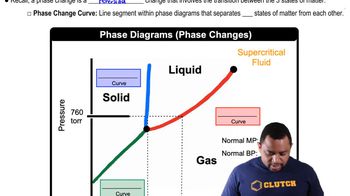
Exothermic and Endothermic Processes

Humidity and Evaporation
Liquids can interact with flat surfaces just as they can with capillary tubes; the cohesive forces within the liquid can be stronger or weaker than the adhesive forces between liquid and surface:
(b) Which of these diagrams, i or ii, rep- resents what happens when water is on a nonpolar surface?
The boiling points, surface tensions, and viscosities of water and several alcohols are listed in the following table:
b. How do you explain the fact that propanol and ethylene glycol have similar molecular weights (60 vs. 62 amu), yet the viscosity of ethylene glycol is more than 10 times larger than propanol?
Name the phase transition in each of the following situations and indicate whether it is exothermic or endothermic: (c) Rubbing alcohol in an open container slowly disappears.
Name the phase transition in each of the following situations and indicate whether it is exothermic or endothermic: (d) Molten lava from a volcano turns into solid rock.
