Textbook Question
If a car tire is filled to a pressure of 32.0 lb/in.2 (psi) measured at 75°F, what will be the tire pressure if the tires heat up to 120°F during driving?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

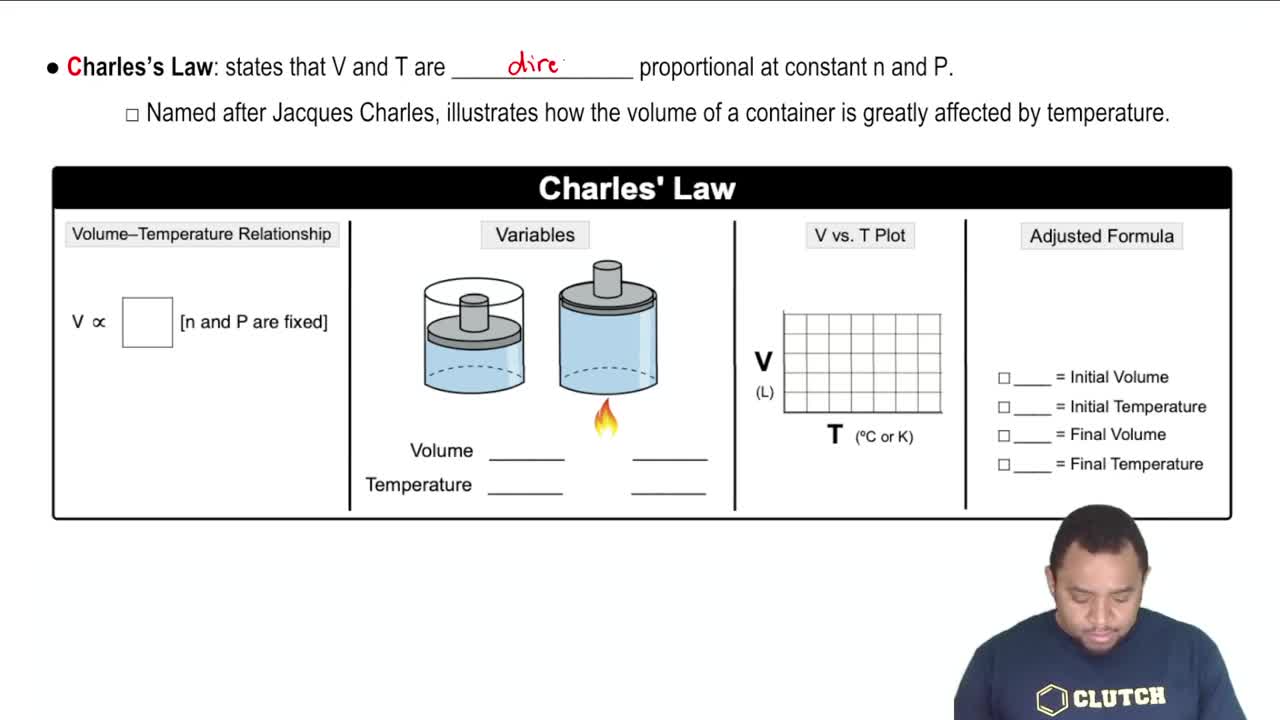
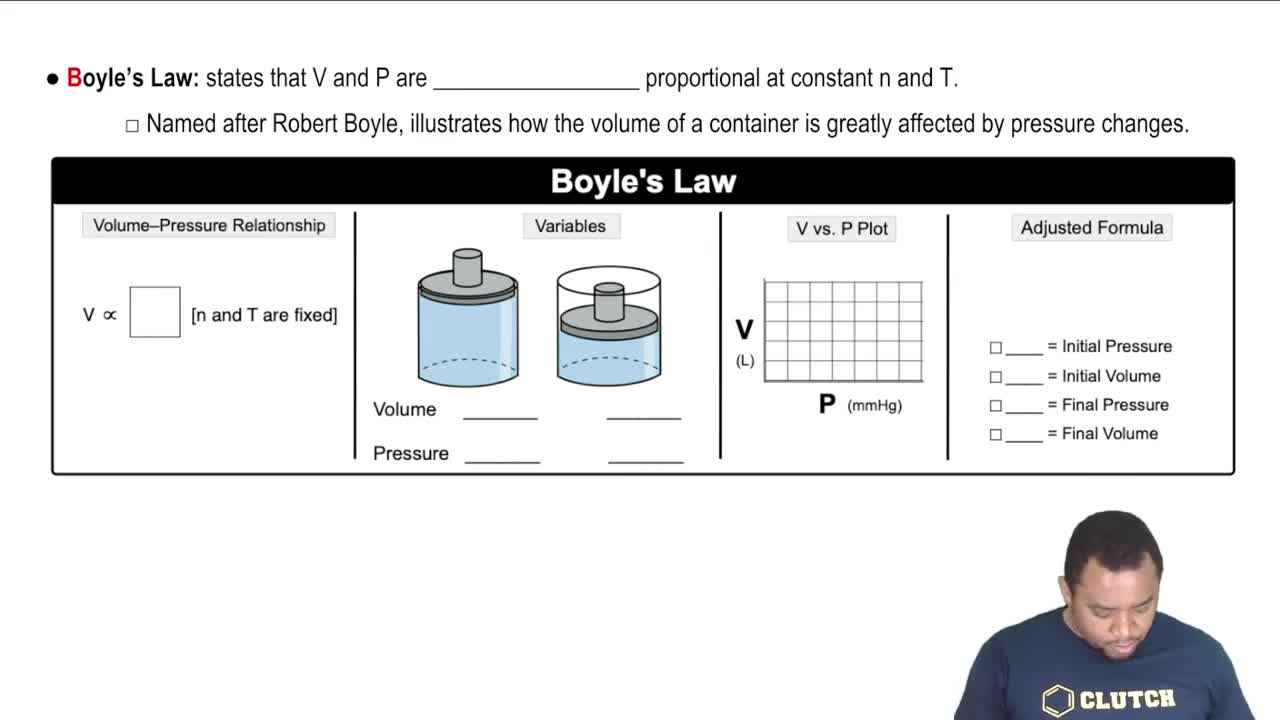
If a car tire is filled to a pressure of 32.0 lb/in.2 (psi) measured at 75°F, what will be the tire pressure if the tires heat up to 120°F during driving?
You have a gas at 25 C confined to a cylinder with a movable piston. Which of the following actions would double the gas pressure? (a) Lifting up on the piston to double the volume while keeping the temperature constant (b) Heating the gas so that its temperature rises from 25 C to 50 C, while keeping the volume constant (c) Pushing down on the piston to halve the volume while keeping the temperature constant.
(b) What is the molar volume of an ideal gas at STP?
(d) If you measure pressure in bars instead of atmospheres, calculate the corresponding value of R in L-bar/mol-K.