Textbook Question
Suppose that on another planet the atmosphere consists of 17% Kr, 38% CH4, and 45% O2. What is the average molar mass at the surface? What is the average molar mass at an altitude at which all the O2 is photodissociated?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
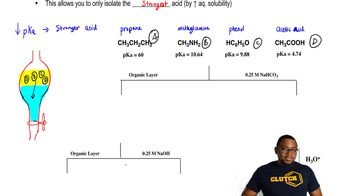

Suppose that on another planet the atmosphere consists of 17% Kr, 38% CH4, and 45% O2. What is the average molar mass at the surface? What is the average molar mass at an altitude at which all the O2 is photodissociated?
Show how Equations 18.7 and 18.9 can be added to give Equation 18.10.
(a) What is the difference between a CFC and an HFC?