Textbook Question
The concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to: H2O(g) → H(g) + OH(g) (b) Using Table 8.3, calculate the wavelength required to cause this dissociation.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
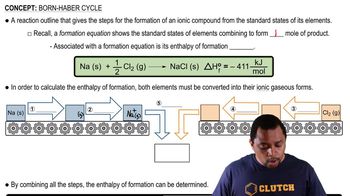

The concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to: H2O(g) → H(g) + OH(g) (b) Using Table 8.3, calculate the wavelength required to cause this dissociation.
The concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to: H2O(g) → H(g) + OH(g)
(c) The hydroxyl radical, OH, can react with ozone, giving the following reactions:
OH(g) + O3(g) → HO2(g) + O2(g)
HO2(g) + O(g) → OH(g) + O2(g)
What overall reaction results from these two elementary reactions? What is the catalyst in the overall reaction? Explain.
The following data were collected for the desturction of O3 by H (O3 + H → O2 + OH) at very low concentrations (b) Calculate the rate constant