In 1986 an electrical power plant in Taylorsville, Georgia, burned 8,376,726 tons of coal, a national record at that time. (b) If 55% of the SO2 could be removed by reaction with powdered CaO to form CaSO3, how many tons of CaSO3 would be produced?

The concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to: H2O(g) → H(g) + OH(g) (b) Using Table 8.3, calculate the wavelength required to cause this dissociation.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Photodissociation
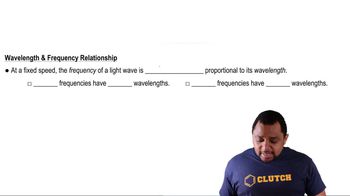
Wavelength and Energy Relationship
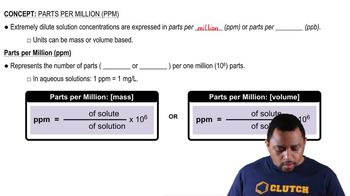
Parts Per Million (ppm)
The water supply for a midwestern city contains the following impurities: coarse sand, finely divided particulates, nitrate ions, trihalomethanes, dissolved phosphorus in the form of phosphates, potentially harmful bacterial strains, dissolved organic substances. Which of the following processes or agents, if any, is effective in removing each of these impurities: coarse sand filtration, activated carbon filtration, aeration, ozonization, precipitation with aluminum hydroxide?
An impurity in water has an extinction coefficient of 3.45⨉103 M-1 cm-1 at 280 nm, its absorption maximum (A Closer Look, p. 576). Below 50 ppb, the impurity is not a problem for human health. Given that most spectrometers cannot detect absorbances less than 0.0001 with good reliability, is measuring the absorbance of a water sample at 280 nm a good way to detect concentrations of the impurity above the 50-ppb threshold?
The concentration of H2O in the stratosphere is about 5 ppm. It undergoes photodissociation according to: H2O(g) → H(g) + OH(g)
(c) The hydroxyl radical, OH, can react with ozone, giving the following reactions:
OH(g) + O3(g) → HO2(g) + O2(g)
HO2(g) + O(g) → OH(g) + O2(g)
What overall reaction results from these two elementary reactions? What is the catalyst in the overall reaction? Explain.
