The ultraviolet spectrum can be divided into three regions based on wavelength: UV-A (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (100–280 nm). (a) Photons from which region have the highest energy and therefore are the most harmful to living tissue? (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (100–280 nm).

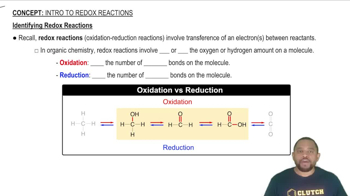
Do the reactions involved in ozone depletion involve changes in the oxidation state of the O atoms? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Ozone Depletion

Oxidation State

Redox Reactions
The ultraviolet spectrum can be divided into three regions based on wavelength: UV-A (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (100–280 nm). (b) In the absence of ozone, which of these three regions, if any, are absorbed by the atmo- sphere?
The ultraviolet spectrum can be divided into three regions based on wavelength: UV-A (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (100–280 nm). (c) When appropriate concentrations of ozone are present in the stratosphere, is all of the UV light absorbed before reaching the Earth’s surface? If not, which region or regions are not filtered out?
Which of the following reactions in the stratosphere cause an increase in temperature there? (a) O(g) + O2(g) → O3+(g) (b) O3*(g) + M(g) → O3(g) + M*(g) (c) O2(g) + hv → 2 O(g) (d) O(g) + N2(g) → NO(g) + N(g) (e) All of the above
(a) What is the difference between chlorofluorocarbons and hydrofluorocarbons?
