The solar power striking Earth every day averages 168 watts per square meter. The highest ever recorded electrical power usage in New York City was 13,200 MW. A record established in July of 2013. Considering that present technology for solar energy conversion is about 10% efficient, from how many square meters of land must sunlight be collected in order to provide this peak power? (For compar- ison, the total area of New York City is 830 km2.)

Explain why Mg(OH)2 precipitates when CO32- ion is added to a solution containing Mg2+.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)

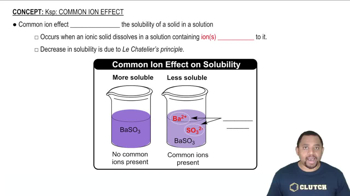
Common Ion Effect
Precipitation Reactions

Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions: (a) The nitric oxide molecule undergoes photodissociation in the upper atmosphere. (b) The nitric oxide molecule undergoes photoionization in the upper atmosphere. (c) Nitric oxide undergoes oxidation by ozone in the stratosphere.
Write balanced chemical equations for each of the following reactions: (d) Nitrogen dioxide dissolves in water to form nitric acid and nitric oxide.
(b) Will Mg(OH)2 precipitate when 4.0 g of Na2CO3 is added to 1.00 L of a solution containing 125 ppm of Mg2+?
(a) The EPA threshold for acceptable levels of lead ions in water is 615 ppb. What is the molarity of an aqueous solution with a concentration of 15 ppb?
(b) Concentrations of lead in the bloodstream are often quoted in units of μg/dL. Averaged over the entire country, the mean concentration of lead in the blood was measured to be 1.6 μg/dL in 2008. Express this concentration in ppb.
