Textbook Question
(a) Explain why BrF4- is square planar, whereas BF4- is tetrahedral.
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance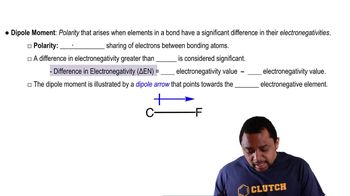


(a) Explain why BrF4- is square planar, whereas BF4- is tetrahedral.
(b) How would you expect the H¬X¬H bond angle to vary in the series H2O, H2S, H2Se? Explain. (Hint: The size of an electron pair domain depends in part on the electronegativity of the central atom.)
(a) Does CS2 have a dipole moment? If so, in which direction does the net dipole point? (b) Does SO2 have a dipole moment? If so, in which direction does the net dipole point?