Sulfur tetrafluoride 1SF42 reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide 1OSF42 according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF41g2 + O21g2¡OSF41g2 The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (a) Balance the equation.
Ch.9 - Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 9, Problem 114b
Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide (OSF4) according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF4(g) + O2(g) → OSF4(g) The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (b) Write a Lewis structure of OSF4 in which the formal charges of all atoms are zero.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the total number of valence electrons in OSF_4. Sulfur (S) has 6 valence electrons, oxygen (O) has 6, and each fluorine (F) has 7. Therefore, the total is 6 (S) + 6 (O) + 4 * 7 (F) = 40 valence electrons.
Place the sulfur (S) atom in the center, as it is the least electronegative element, and arrange the oxygen (O) and four fluorine (F) atoms around it.
Draw single bonds between the central sulfur atom and each of the surrounding atoms (O and F). This uses up 5 bonds * 2 electrons/bond = 10 electrons.
Distribute the remaining 30 electrons to satisfy the octet rule for the surrounding atoms, starting with the more electronegative atoms (O and F). Each F atom should have 6 more electrons to complete its octet, using 24 electrons in total.
Assign the remaining electrons to the central sulfur atom. Check the formal charges: S should have 0 formal charge with 6 electrons around it, O should have 0 formal charge with 8 electrons around it, and each F should have 0 formal charge with 8 electrons around it.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lewis Structures
Lewis structures are diagrams that represent the bonding between atoms in a molecule and the lone pairs of electrons that may exist. They help visualize the arrangement of electrons and the connectivity of atoms, allowing chemists to predict molecular geometry and reactivity. In constructing a Lewis structure, one must account for the total number of valence electrons and ensure that each atom achieves a stable electron configuration, typically resembling that of noble gases.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lewis Dot Structures: Ions
Formal Charge
Formal charge is a concept used to determine the distribution of electrons in a molecule. It is calculated by taking the number of valence electrons in an atom, subtracting the number of non-bonding electrons, and half the number of bonding electrons. A formal charge of zero on all atoms in a molecule is often desirable, as it indicates a more stable structure. Understanding formal charges is crucial for drawing accurate Lewis structures and predicting molecular stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formal Charge
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is influenced by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom, which can affect the molecule's shape and properties. The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory is commonly used to predict molecular geometry, helping to understand how the arrangement of atoms can impact reactivity and interactions with other molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course
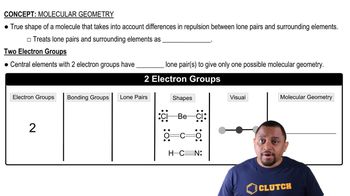
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur tetrafluoride monoxide (OSF4) according to the following unbalanced reaction: SF4(g) + O2(g) → OSF4(g) The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a central S atom. (c) Use average bond enthalpies (Table 8.3) to estimate the enthalpy of the reaction. Is it endothermic or exothermic?
Textbook Question
Sulfur tetrafluoride 1SF42 reacts slowly with O2 to form sulfur
tetrafluoride monoxide 1OSF42 according to the following
unbalanced reaction:
SF41g2 + O21g2¡OSF41g2
The O atom and the four F atoms in OSF4 are bonded to a
central S atom.
(e) For each of the molecules you drew in part (d), state how many
fluorines are equatorial and how many are axial.
1
views
Textbook Question
The phosphorus trihalides 1PX32 show the following variation in the bond angle X¬P¬X: PF3, 96.3°; PCl3, 100.3°; PBr3, 101.0°; PI3, 102.0°. The trend is generally attributed to the change in the electronegativity of the halogen. (b) What is the general trend in the X¬P¬X angle as the halide electronegativity increases?
