(a) An AB6 molecule has no lone pairs of electrons on the A atom. What is its molecular geometry? (c) For the AB4 molecule in part (b), predict the molecular geometry.
Ch.9 - Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 9, Problem 19
In which of these molecules or ions does the presence of nonbonding electron pairs produce an effect on the molecular shape? (a) CO2, (b) CH2Br2, (c) OF2, (d) BCl3, (e) SF6.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of molecular shape and the role of nonbonding electron pairs. Nonbonding electron pairs, also known as lone pairs, can influence the geometry of a molecule by repelling bonding pairs of electrons, which can alter the molecular shape.
Step 2: Analyze each molecule or ion to determine the presence of nonbonding electron pairs on the central atom. Use the Lewis structure to identify lone pairs.
Step 3: For each molecule or ion, apply the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory to predict the molecular shape. VSEPR theory states that electron pairs around a central atom will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, affecting the shape.
Step 4: Evaluate the effect of any nonbonding electron pairs on the molecular shape. Nonbonding pairs exert greater repulsive force than bonding pairs, potentially altering the expected geometry.
Step 5: Identify which molecules or ions have their molecular shape affected by nonbonding electron pairs based on your analysis.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
VSEPR Theory
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory is a model used to predict the geometry of individual molecules based on the repulsion between electron pairs in the valence shell of the central atom. According to this theory, electron pairs, whether bonding or nonbonding, will arrange themselves to minimize repulsion, thus influencing the overall shape of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course
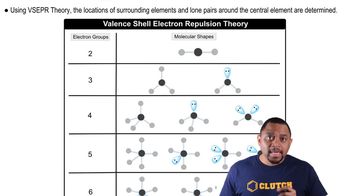
Molecular Shapes and VSEPR
Nonbonding Electron Pairs
Nonbonding electron pairs, also known as lone pairs, are pairs of valence electrons that are not involved in bonding with other atoms. These lone pairs occupy space around the central atom and can significantly affect molecular geometry by repelling bonding pairs, leading to distortions in the expected shape of the molecule.
Recommended video:
Guided course
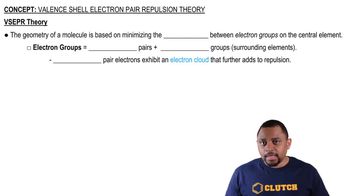
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
Molecular Geometry
Molecular geometry refers to the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a molecule. It is determined by the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs around the central atom, which influences bond angles and overall shape. Understanding molecular geometry is crucial for predicting the physical and chemical properties of substances.
Recommended video:
Guided course
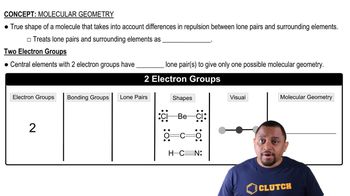
Molecular Geometry with Two Electron Groups
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(b) An AB4 molecule has two lone pairs of electrons on the A atom (in addition to the four B atoms). What is the electron-domain geometry around the A atom?
2
views
Textbook Question
Would you expect the nonbonding electron-pair domain in NCl3 to be greater or smaller in size than the corresponding one in PCl3?
1
views
Textbook Question
In which of the following molecules can you confidently predict the bond angles about the central atom, and for which would you be a bit uncertain? Explain in each case. (a) H2S, (b) BCl3, (c) CH3I, (d) CBr4, (e) TeBr4.
Textbook Question
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (a) (CH3)2S (c) BF3 (d) SO2
Textbook Question
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (b) HCN
