Textbook Question
In which of the following molecules can you confidently predict the bond angles about the central atom, and for which would you be a bit uncertain? Explain in each case. (a) H2S, (b) BCl3, (c) CH3I, (d) CBr4, (e) TeBr4.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

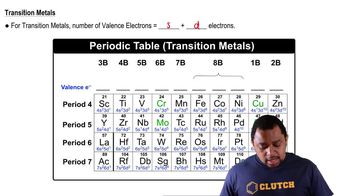
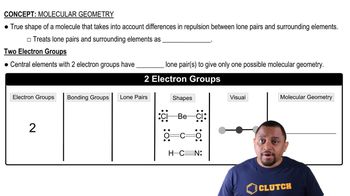
In which of the following molecules can you confidently predict the bond angles about the central atom, and for which would you be a bit uncertain? Explain in each case. (a) H2S, (b) BCl3, (c) CH3I, (d) CBr4, (e) TeBr4.
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (a) (CH3)2S (c) BF3 (d) SO2
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (b) HCN