Textbook Question
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (a) (CH3)2S (c) BF3 (d) SO2

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
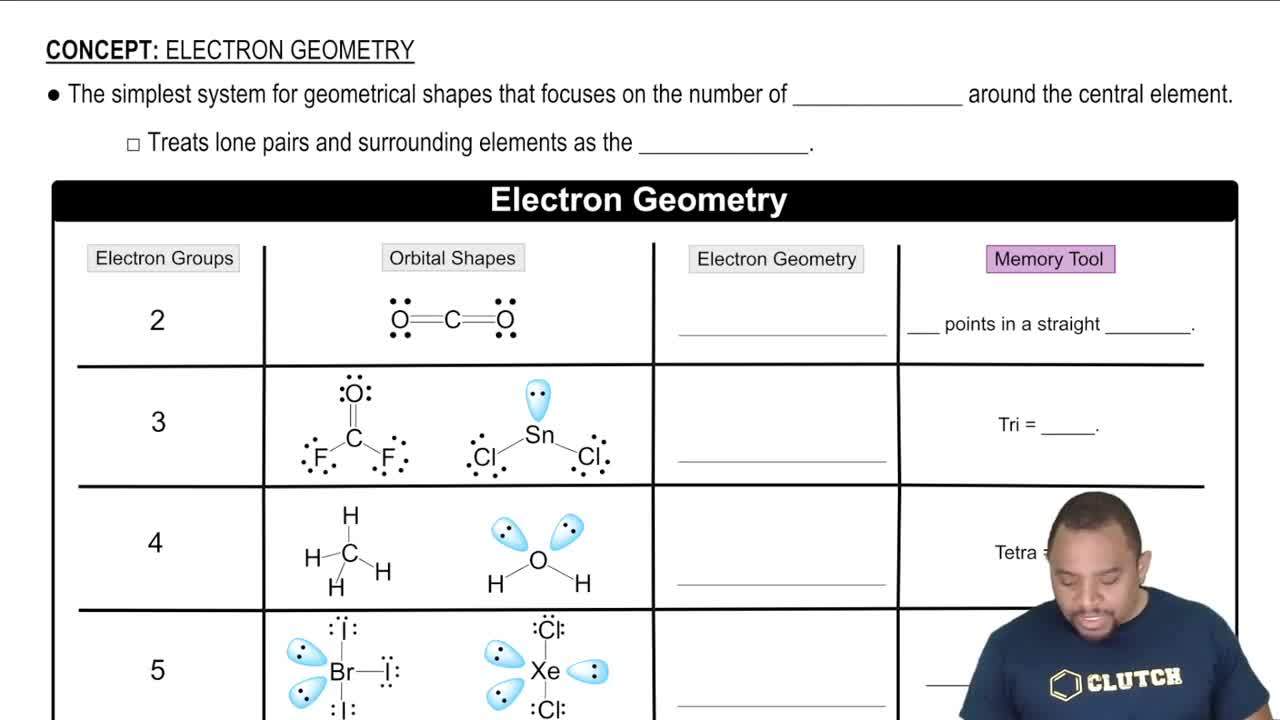
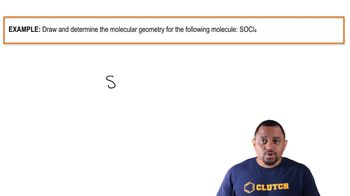
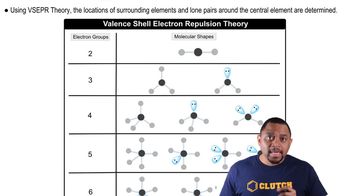
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (a) (CH3)2S (c) BF3 (d) SO2
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (b) HCN
How many nonbonding electron pairs are there in each of the following molecules: (b) HCN
Give the electron-domain and molecular geometries for the following molecules and ions: (a) BeF2