Dichloroethylene (C2H2Cl2) has three forms (isomers), each of which is a different substance. (b) Which of these isomers has a zero dipole moment?

For each statement, indicate whether it is true or false. (a) In order to make a covalent bond, the orbitals on each atom in the bond must overlap. (b) A p orbital on one atom cannot make a bond to an s orbital on another atom.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Covalent Bonding
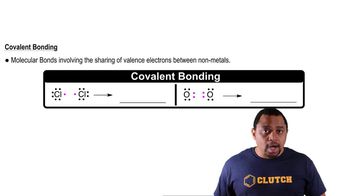
Orbital Overlap
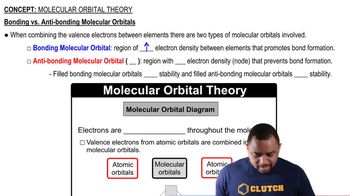
Types of Atomic Orbitals
Dichloroethylene (C2H2Cl2) has three forms (isomers), each of which is a different substance. (c) How many isomeric forms can chloroethylene, C2H3Cl, have? Would they be expected to have dipole moments?
Dihydroxybenzene, C6H6O2, exists in three forms (isomers) called ortho, meta, and para:
Which of these has a nonzero dipole moment?
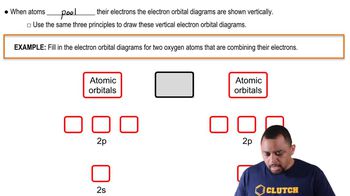
Draw sketches illustrating the overlap between the following orbitals on two atoms: (a) the 2s orbital on each atom
Draw sketches illustrating the overlap between the following orbitals on two atoms: (b) the 2pz orbital on each atom (assume both atoms are on the z-axis) (c) the 2s orbital on one atom and the 2pz orbital on the other atom.
For each statement, indicate whether it is true or false. (d) Nonbonding electron pairs cannot occupy a hybrid orbital.
