Textbook Question
(a) Consider the following two molecules: PCl3 and BCl3. Which molecule has a nonzero dipole moment?
1
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
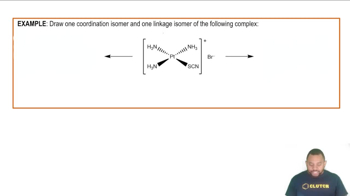

(a) Consider the following two molecules: PCl3 and BCl3. Which molecule has a nonzero dipole moment?
Predict whether each of the following molecules is polar or nonpolar: (a) IF, (b) CS2, (c) SO3, (d) PCl3, (e) SF6, (f) IF5.
Predict whether each of the following molecules is polar or nonpolar: (a) CCl4, (b) NH3, (c) SF4, (d) XeF4, (e) CH3Br, (f) GaH3.
Dichloroethylene (C2H2Cl2) has three forms (isomers), each of which is a different substance. (c) How many isomeric forms can chloroethylene, C2H3Cl, have? Would they be expected to have dipole moments?
Dihydroxybenzene, C6H6O2, exists in three forms (isomers) called ortho, meta, and para:
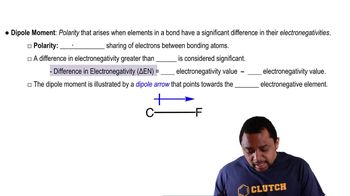
Which of these has a nonzero dipole moment?