Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:(a) Draw all of the resonance structures of naphthalene. How many are there?

(a) Which of these compounds is an exception to the octet rule: carbon dioxide, water, ammonia, phosphorus trifluoride, or arsenic pentafluoride?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
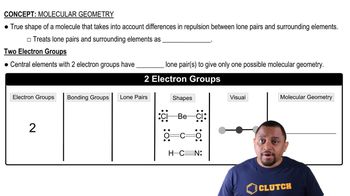
Key Concepts
Octet Rule

Exceptions to the Octet Rule

Molecular Geometry and Bonding
Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:
(b) Do you expect the C—C bond lengths in the molecule to be similar to those of C—C single bonds, C ═C double bonds, or intermediate between C—C single and C ═C double bonds?
Mothballs are composed of naphthalene, C10H8, a molecule that consists of two six-membered rings of carbon fused along an edge, as shown in this incomplete Lewis structure:
(c) Not all of the C—C bond lengths in naphthalene are equivalent. Based on your resonance structures, how many C—C bonds in the molecule do you expect to be shorter than the others?
(b) Which of these compounds or ions is an exception to the octet rule: borohydride (BH4-), borazine (B3N3H6, which is analogous to benzene with alternating B and N in the ring), or boron trichloride?
