Textbook Question
Based on their positions in the periodic table, predict which atom of the following pairs will have the smaller first ionization energy: (a) Br, Kr (b) C, Ca (c) Li, Rb (d) S, Ge (e) Al, B.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance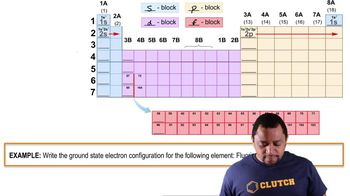
Based on their positions in the periodic table, predict which atom of the following pairs will have the smaller first ionization energy: (a) Br, Kr (b) C, Ca (c) Li, Rb (d) S, Ge (e) Al, B.
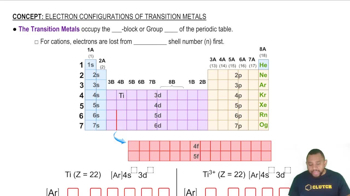
Give examples of transition metal ions with +3 charge that have an electron configuration of nd5 (n = 3, 4, 5...).