Textbook Question
Give examples of transition metal ions with +3 charge that have an electron configuration of nd5 (n = 3, 4, 5...).

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

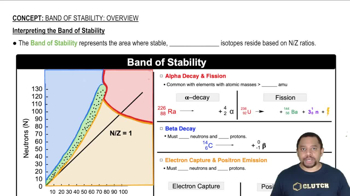
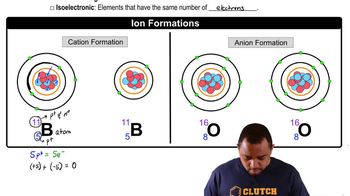
Give examples of transition metal ions with +3 charge that have an electron configuration of nd5 (n = 3, 4, 5...).