Methanol (CH3OH) is used as a fuel in race cars. (c) Calculate the heat produced by combustion per liter of methanol. Methanol has a density of 0.791 g/mL.

Without doing any calculations, predict the sign of _x001F_H for each of the following reactions: (a) 2 NO2(g) → N2O4(g) (b) 2 F(g) → F2(g) (c) Mg2+(g) + 2 Cl-(g) → MgCl2(s) (d) HBr(g) → H(g) + Br(g)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Enthalpy Change (_x001F_H)

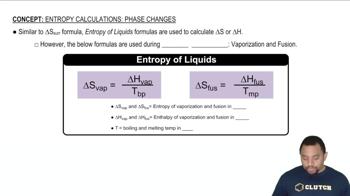
Phase Changes and Stability
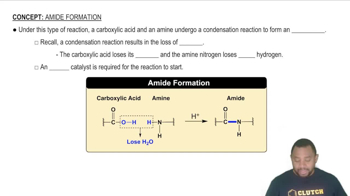
Bond Formation and Breaking
Methanol (CH3OH) is used as a fuel in race cars. (d) Calculate the mass of CO2 produced per kJ of heat emitted.
Use bond enthalpies in Table 5.4 to estimate H for each of the following reactions: (a)
(a) The nitrogen atoms in an N2 molecule are held together by a triple bond; use enthalpies of formation in Appendix C to estimate the enthalpy of this bond, D(N‚N). (b) Consider the reaction between hydrazine and hydrogen to produce ammonia, N2H41g2 + H21g2¡2 NH31g2. Use enthalpies of formation and bond enthalpies to estimate the enthalpy of the nitrogen– nitrogen bond in N2H4. (c) Based on your answers to parts (a) and (b), would you predict that the nitrogen–nitrogen bond in hydrazine is weaker than, similar to, or stronger than the bond in N2 ?
