In a thermodynamic study, a scientist focuses on the properties of a solution in an apparatus as illustrated. A solution is continuously flowing into the apparatus at the top and out at the bottom, such that the amount of solution in the apparatus is constant with time. (b) If the inlet and outlet were closed, what type of system would it be
Ch.5 - Thermochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 5, Problem 23c
(c) By what means can the internal energy of a closed system increase?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that internal energy (U) of a closed system can change through heat (q) and work (w) based on the first law of thermodynamics.
Recall the first law of thermodynamics: \( \Delta U = q + w \), where \( \Delta U \) is the change in internal energy.
Identify that internal energy increases when the system absorbs heat (q > 0) from the surroundings.
Recognize that internal energy also increases when work is done on the system (w > 0), such as compression work.
Conclude that both heat absorption and work done on the system contribute to an increase in internal energy.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
51sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Internal Energy
Internal energy is the total energy contained within a system, encompassing both kinetic and potential energy of the particles. It is a state function, meaning it depends only on the current state of the system, not on how it reached that state. Changes in internal energy can be observed through heat transfer and work done on or by the system.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Internal Energy
First Law of Thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. In a closed system, the change in internal energy is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system. This principle is fundamental in understanding how energy transfers affect a system's internal energy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
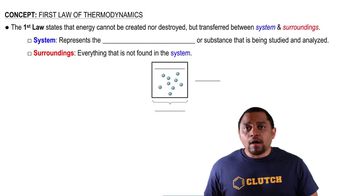
First Law of Thermodynamics
Heat and Work
Heat and work are two primary means by which energy can be transferred into or out of a system. Heat refers to energy transfer due to temperature differences, while work involves energy transfer resulting from forces acting over distances. Both processes can lead to an increase in a system's internal energy, depending on the direction of energy flow.
Recommended video:
Guided course
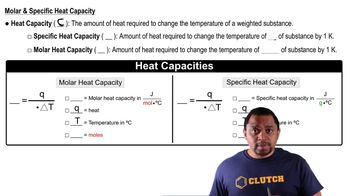
Heat Capacity
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
(a) According to the first law of thermodynamics, what quantity is conserved?
2
views
Textbook Question
(b) What is meant by the internal energy of a system?
Textbook Question
Calculate ΔE and determine whether the process is endothermic or exothermic for the following cases: (a) q = 0.763 kJ and w = -840 J.
Textbook Question
Calculate ΔE and determine whether the process is endothermic or exothermic for the following cases: (b) A system releases 66.1 kJ of heat to its surroundings while the surroundings do 44.0 kJ of work on the system.
