In a thermodynamic study, a scientist focuses on the properties of a solution in an apparatus as illustrated. A solution is continuously flowing into the apparatus at the top and out at the bottom, such that the amount of solution in the apparatus is constant with time. (a) Is the solution in the apparatus a closed system, open system, or isolated system?
Ch.5 - Thermochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 5, Problem 23a
(a) According to the first law of thermodynamics, what quantity is conserved?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
The first law of thermodynamics is a version of the law of conservation of energy, adapted for thermodynamic systems.
It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system.
The first law is often expressed as \( \Delta U = Q - W \), where \( \Delta U \) is the change in internal energy of the system, \( Q \) is the heat added to the system, and \( W \) is the work done by the system.
According to this law, the total energy of an isolated system is constant.
Therefore, the quantity that is conserved according to the first law of thermodynamics is energy.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The First Law of Thermodynamics, also known as the law of energy conservation, states that energy cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system. Instead, energy can only be transformed from one form to another. This principle is fundamental in understanding how energy flows in physical and chemical processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
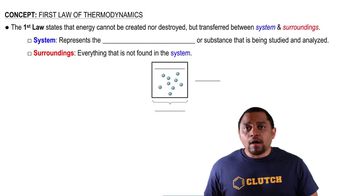
First Law of Thermodynamics
Internal Energy
Internal energy is the total energy contained within a system, including kinetic and potential energy at the molecular level. According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, any change in the internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system on its surroundings. This concept is crucial for analyzing thermodynamic processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Internal Energy
Work and Heat
In thermodynamics, work and heat are two ways energy can be transferred between a system and its surroundings. Work refers to energy transfer that occurs when a force is applied over a distance, while heat is the energy transferred due to a temperature difference. Understanding these concepts is essential for applying the First Law of Thermodynamics to real-world scenarios.
Recommended video:
Guided course
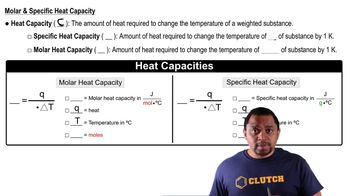
Heat Capacity
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
In a thermodynamic study, a scientist focuses on the properties of a solution in an apparatus as illustrated. A solution is continuously flowing into the apparatus at the top and out at the bottom, such that the amount of solution in the apparatus is constant with time. (b) If the inlet and outlet were closed, what type of system would it be
1
views
Textbook Question
(b) What is meant by the internal energy of a system?
Textbook Question
(c) By what means can the internal energy of a closed system increase?
