Write 'true' or 'false' for each statement. (b) If the reaction 2 O3(g) → 3 O2(g) goes to completion and all O3 is converted to O2, then the mass of O3 at the beginning of the reaction must be the same as the mass of O2 at the end of the reaction.
Ch.3 - Chemical Reactions and Reaction Stoichiometry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 3, Problem 11c
Balance the following equations: (c) Al(OH)3(s) + H2SO4(l) → Al2(SO4)3(s) + H2O(l)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the number of each type of atom on both sides of the equation.
Start by balancing the aluminum (Al) atoms. There are 2 Al atoms in Al2(SO4)3, so you need 2 Al(OH)3 on the reactant side.
Next, balance the sulfate (SO4) groups. There are 3 SO4 groups in Al2(SO4)3, so you need 3 H2SO4 on the reactant side.
Balance the hydrogen (H) atoms. Count the H atoms from both Al(OH)3 and H2SO4 on the reactant side and ensure they match the number of H atoms in H2O on the product side.
Finally, balance the oxygen (O) atoms. Check that the total number of O atoms on both sides of the equation is equal.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves ensuring that the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This is based on the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. Coefficients are used to adjust the quantities of reactants and products to achieve balance.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Types of Chemical Reactions
Understanding the types of chemical reactions, such as double displacement, is crucial for balancing equations. In a double displacement reaction, two compounds exchange ions to form new compounds. Recognizing the reactants and products in the given equation helps in predicting the correct products and their states.
Recommended video:
Guided course
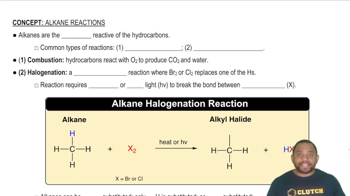
Common Types of Alkane Reactions
States of Matter in Reactions
The states of matter (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous) are important in chemical equations as they provide information about the physical state of the reactants and products. In the given equation, Al(OH)3 is a solid, H2SO4 is a liquid, and the products include a solid and a liquid. This information can influence the reaction conditions and the balancing process.
Recommended video:
Guided course
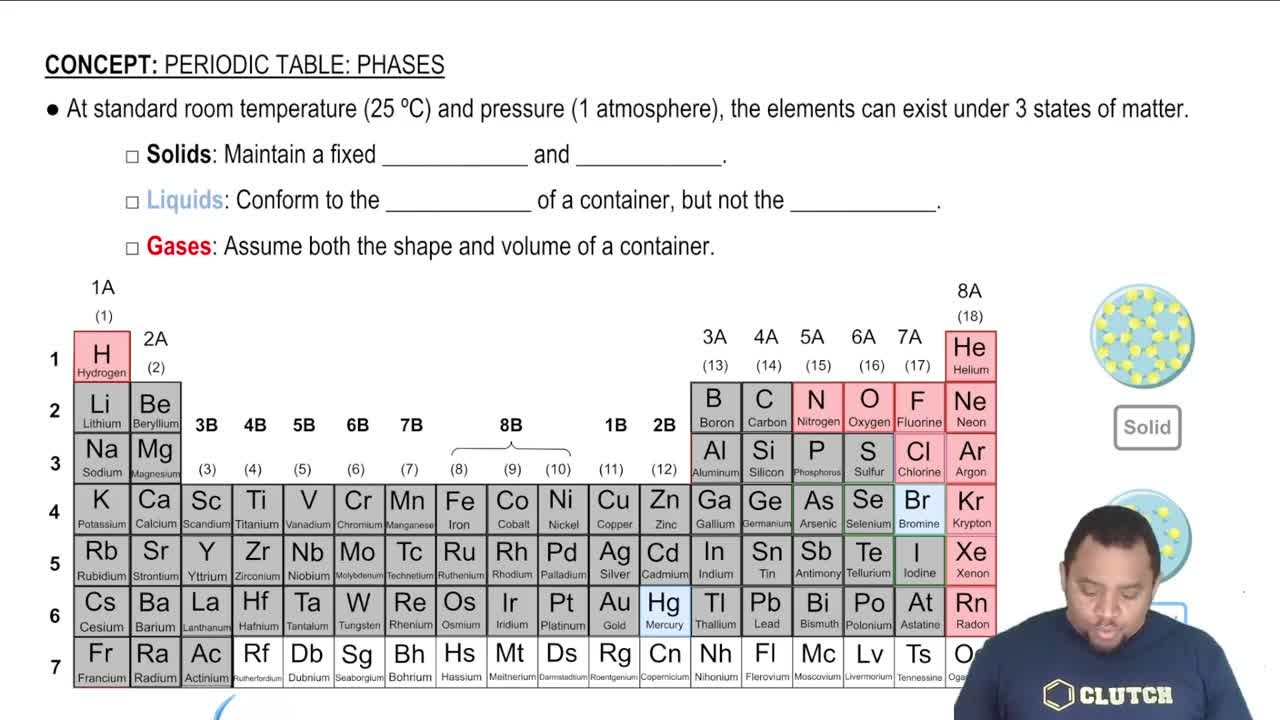
Element States of Matter
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
A key step in balancing chemical equations is correctly identifying the formulas of the reactants and products. For example, consider the reaction between calcium oxide, CaO(s), and H2O1l2 to form aqueous calcium hydroxide. (b) Is it possible to balance the equation if you incorrectly identify the product as CaOH1aq2, and if so, what is the equation?
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations:
(a) HClO4(aq) + P4O10(s) → HPO3(aq) + Cl2O7(l)
(b) Au2S3(s + H2(g) → Au(s) + H2S(g)
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations: (c) Ba3N2(s) + H2O(aq) → Ba(OH)2(aq) + NH3(g)
Textbook Question
Balance the following equations: (d) Na2CO3(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
