Write 'true' or 'false' for each statement. (a) We balance chemical equations as we do because energy must be conserved.

(a) If an automobile travels 350 km with a gas mileage of 9.0 km/L, how many kilograms of CO2 are produced? Assume that the gasoline is composed of octane, C8H181l2, whose density is 0.692 g/mL. (b) Repeat the calculation for a truck that has a gas mileage of 2 km/L.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Stoichiometry

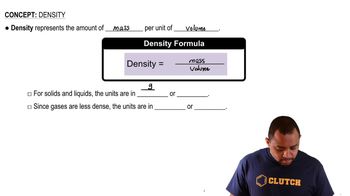
Density and Volume Calculations
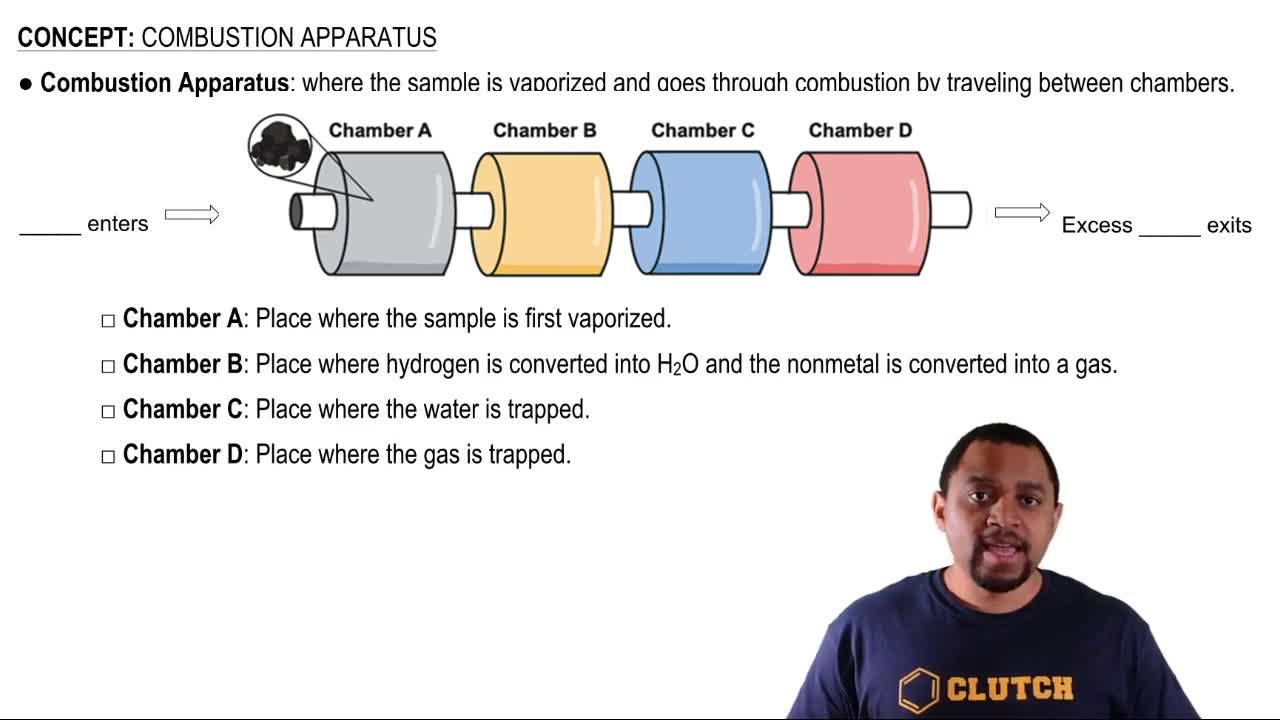
Combustion Reactions
Write 'true' or 'false' for each statement. (b) If the reaction 2 O3(g) → 3 O2(g) goes to completion and all O3 is converted to O2, then the mass of O3 at the beginning of the reaction must be the same as the mass of O2 at the end of the reaction.
A key step in balancing chemical equations is correctly identifying the formulas of the reactants and products. For example, consider the reaction between calcium oxide, CaO(s), and H2O1l2 to form aqueous calcium hydroxide. (b) Is it possible to balance the equation if you incorrectly identify the product as CaOH1aq2, and if so, what is the equation?
Balance the following equations: (c) Al(OH)3(s) + H2SO4(l) → Al2(SO4)3(s) + H2O(l)
Balance the following equations:
(a) HClO4(aq) + P4O10(s) → HPO3(aq) + Cl2O7(l)
(b) Au2S3(s + H2(g) → Au(s) + H2S(g)
Balance the following equations: (c) Ba3N2(s) + H2O(aq) → Ba(OH)2(aq) + NH3(g)
