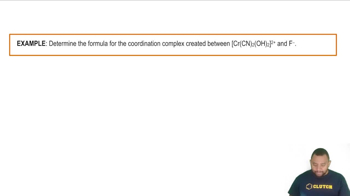
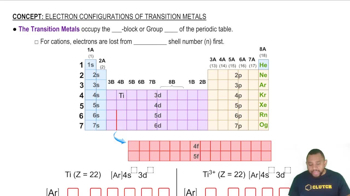
Textbook Question
The coordination complex [Cr(CO)6] forms colorless, diamagnetic crystals that melt at 90 °C
a. What is the oxidation number of chromium in this compound?
d. Write the name for [Cr(CO)6] using the nomenclature rules for coordination compounds.