Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 21
Give a reason why hydrogen might be placed along with the Group 1A elements of the periodic table.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the electronic configuration of hydrogen. Hydrogen has one electron in its outer shell, similar to the Group 1A elements (alkali metals) which also have one electron in their outermost shell.
Step 2: Consider the reactivity of hydrogen. Like alkali metals, hydrogen can lose its single electron to form a positive ion (H⁺), which is a characteristic behavior of Group 1A elements.
Step 3: Examine the chemical properties. Hydrogen can form compounds by sharing or transferring its electron, similar to how alkali metals form ionic compounds by losing their outer electron.
Step 4: Analyze the position in the periodic table. Hydrogen is placed at the top of Group 1A due to its similar electronic configuration, despite being a non-metal.
Step 5: Reflect on historical context. Historically, hydrogen was grouped with alkali metals due to its similar properties, although it is unique and often considered separately in modern chemistry.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrogen's Position in the Periodic Table
Hydrogen is often placed at the top of Group 1A (alkali metals) due to its similar electron configuration, having one electron in its outer shell. This similarity suggests that hydrogen can exhibit similar chemical properties, such as forming +1 ions, akin to alkali metals. However, hydrogen is unique and does not share all properties with these metals.
Recommended video:
Guided course
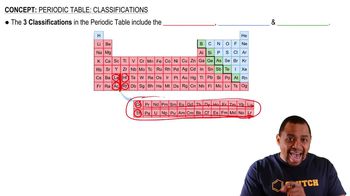
Periodic Table Classifications
Alkali Metals Characteristics
Alkali metals, found in Group 1A, are characterized by their high reactivity, especially with water, and their tendency to lose one electron to form positive ions. This reactivity is due to their low ionization energies, which allow them to easily lose their outermost electron. Hydrogen, while not a metal, can also lose its single electron, leading to similar reactivity patterns under certain conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
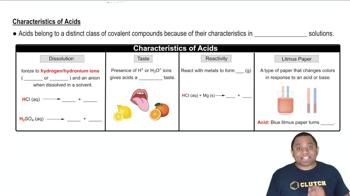
Acid Characteristics
Chemical Behavior of Hydrogen
Hydrogen exhibits both metallic and non-metallic properties, allowing it to participate in a variety of chemical reactions. It can act as a reducing agent and form covalent bonds, unlike typical alkali metals. This dual behavior makes hydrogen versatile, enabling it to fit into discussions about Group 1A elements, despite its distinct non-metallic nature.
Recommended video:
Guided course
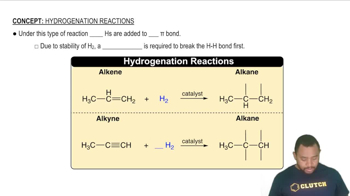
Hydrogenation Reactions
Related Practice
