Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents: MnO4-(aq) + Br-(aq) → MnO2(s) + BrO3-(aq) (basic solution)

Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) The cathode is the electrode at which oxidation takes place. (b) A galvanic cell is another name for a voltaic cell. (c) Electrons flow spontaneously from anode to cathode in a voltaic cell.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Electrochemical Cells
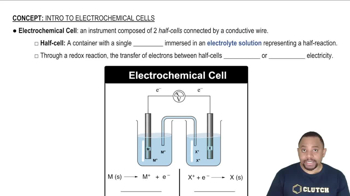
Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells

Oxidation and Reduction

Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (Recall that the O atoms in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, have an atypical oxidation state.) (a) NO2-(aq) + Cr2O72-(aq) → Cr3+(aq) + NO3-(aq) (acidic solution) (b) S(s) + HNO3(aq) → H2SO3(aq) + N2O(g) (acidic solution) (c) Cr2O72- (aq) + CH3OH(aq) → HCOOH(aq) + Cr3+(aq) (acidic solution) (d) BrO3-(aq) + N2H4(g) → Br-(aq) + N2(g) (acidic solution)
Complete and balance the following equations, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. (Recall that the O atoms in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, have an atypical oxidation state.) H2O21aq2 + ClO21aq2 ¡ ClO2-1aq2 + O21g2 (basic solution)
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (c) A salt bridge or permeable barrier is necessary to allow a voltaic cell to operate.
A voltaic cell similar to that shown in Figure 20.5 is constructed. One electrode half-cell consists of a silver strip placed in a solution of AgNO3, and the other has an iron strip placed in a solution of FeCl2. The overall cell reaction is Fe1s2 + 2 Ag+1aq2 ¡ Fe2+1aq2 + 2 Ag1s2 (f) In which directions do the cations and anions migrate through the solution?
