The capacity of batteries such as the typical AA alkaline battery is expressed in units of milliamp-hours (mAh). An AA alkaline battery yields a nominal capacity of 2850 mAh. (b) The starting voltage of a fresh alkaline battery is 1.55 V. The voltage decreases during discharge and is 0.80 V when the battery has delivered its rated capacity. If we assume that the voltage declines linearly as current is withdrawn, estimate the total maximum electrical work the battery could perform during discharge.
Ch.20 - Electrochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 20, Problem 106c
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (c) If you react two thiols to make a disulfide, are you oxidizing or reducing the thiols?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
insert step 1> Identify the functional groups involved in the reaction: thiols (R-SH) and disulfides (R-S-S-R).
insert step 2> Understand the concept of oxidation and reduction: Oxidation involves the loss of electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons.
insert step 3> Analyze the change in oxidation state of sulfur: In thiols (R-SH), sulfur is in a lower oxidation state compared to disulfides (R-S-S-R).
insert step 4> Determine the electron transfer: When two thiols form a disulfide, each sulfur atom loses an electron, indicating oxidation.
insert step 5> Conclude that the reaction of two thiols to form a disulfide involves the oxidation of the thiols.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation and Reduction
Oxidation and reduction are chemical processes that involve the transfer of electrons between substances. Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons, while reduction involves the gain of electrons. In organic chemistry, oxidation often results in an increase in the number of bonds to oxygen or a decrease in bonds to hydrogen, while reduction typically has the opposite effect.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation and Reduction Reactions
Thiols and Disulfides
Thiols are organic compounds characterized by the presence of a sulfhydryl group (-SH), which can participate in redox reactions. When two thiols react, they can form a disulfide bond (R-S-S-R), which involves the coupling of two sulfur atoms. This transformation is significant in biochemistry, as disulfide bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing protein structures.
Recommended video:
Guided course
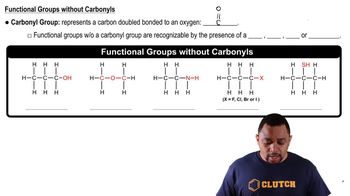
Non-Carbonyl Functional Groups
Redox Reaction in Thiol to Disulfide Conversion
The conversion of two thiols into a disulfide bond is classified as an oxidation reaction. During this process, each thiol loses a hydrogen atom (as H+ and e-), resulting in the formation of the disulfide bond. Thus, the thiols are oxidized, while the disulfide formed is a more oxidized state of sulfur compared to the thiols.
Recommended video:
Guided course
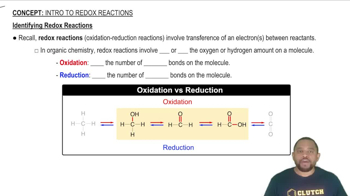
Identifying Redox Reactions
Related Practice
Textbook Question
4
views
Textbook Question
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (b) What is the oxidation state of sulfur in a disulfide?
Textbook Question
Calculate the number of kilowatt-hours of electricity required to produce 1.0 * 103 kg (1 metric ton) of aluminum by electrolysis of Al3+ if the applied voltage is 4.50 V and the process is 45% efficient.
