
If you wanted to convert a disulfide to two thiols, should you add a reducing agent or an oxidizing agent to the solution?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Disulfide Bonds
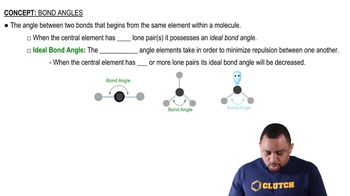
Reducing Agents

Oxidizing Agents

The capacity of batteries such as the typical AA alkaline battery is expressed in units of milliamp-hours (mAh). An AA alkaline battery yields a nominal capacity of 2850 mAh. (b) The starting voltage of a fresh alkaline battery is 1.55 V. The voltage decreases during discharge and is 0.80 V when the battery has delivered its rated capacity. If we assume that the voltage declines linearly as current is withdrawn, estimate the total maximum electrical work the battery could perform during discharge.
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (b) What is the oxidation state of sulfur in a disulfide?
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (c) If you react two thiols to make a disulfide, are you oxidizing or reducing the thiols?
