Textbook Question
(c) What process occurs at the anode in the electrolysis of molten NaCl?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


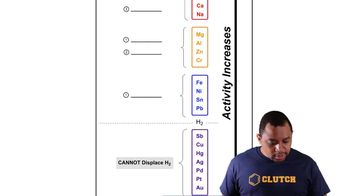
(c) What process occurs at the anode in the electrolysis of molten NaCl?
(d) Why is sodium metal not obtained when an aqueous solution of NaCl undergoes electrolysis?
(a) A Cr3+(aq) solution is electrolyzed, using a current of 7.60 A. What mass of Cr(s) is plated out after 2.00 days?
(b) What amperage is required to plate out 0.250 mol Cr from a Cr3+ solution in a period of 8.00 h?