From the molecular structures shown here, identify the one that corresponds to each of the following species: (a) chlorine gas; (b) propane; (c) nitrate ion; (d) sulfur trioxide; (e) methyl chloride, CH3Cl.
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 107a
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the first column of the table.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the cation and anion for each compound.
For 'Lithium oxide', the cation is Li+ and the anion is O2-.
For 'Fe2+ PO43-', the cation is Fe2+ and the anion is PO43-.
For 'Al2(SO4)3', the cation is Al3+ and the anion is SO42-.
For 'Copper(II) nitrate', the cation is Cu2+ and the anion is NO3-.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed from the electrostatic attraction between cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions). They typically consist of a metal and a non-metal, where the metal donates electrons to become a cation, while the non-metal accepts electrons to become an anion. Understanding the formation and naming conventions of these compounds is essential for completing the table.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Nomenclature of Ions
The nomenclature of ions involves specific rules for naming cations and anions. Cations are usually named after their parent element, often with the addition of a Roman numeral to indicate their charge, while anions typically have names derived from their parent element with suffixes like '-ide', '-ate', or '-ite' depending on their composition. Familiarity with these naming conventions is crucial for accurately filling in the table.
Recommended video:
Guided course
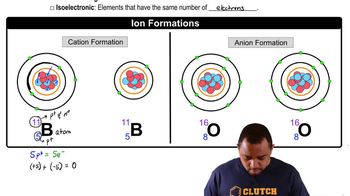
Ion Formation
Chemical Formulas
Chemical formulas represent the composition of ionic compounds, indicating the types and ratios of ions present. The formula is derived from the charges of the cations and anions, ensuring that the overall charge of the compound is neutral. Understanding how to derive and interpret these formulas is key to completing the first column of the table correctly.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Skeletal Formula
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the third column of the table.
Complete the fourth column of the table.
Textbook Question
Consider a sample of calcium carbonate in the form of a cubemeasuring 2.005 in. on each edge. If the sample has a densityof 2.71 g>cm3, how many oxygen atoms does it contain?
Textbook Question
Cyclopropane is an interesting hydrocarbon. Instead of having three carbons in a row, the three carbons form a ring, as shown in this perspective drawing (see Figure 2.18 for a prior example of this kind of drawing):
Cyclopropane was at one time used as an anesthetic, but its use was discontinued, in part because it is highly flammable. (a) How does it differ from that of propane?
2
views
