The solubility of CaCO3 is pH dependent. (b) Use the Kb expression for the CO32- ion to determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ Ca2+(aq) + HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq)
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 101
What is the pH of a 1 * 10^-3 M solution of Na3PO4? You can ignore the formation of H2PO4- and H3PO4^2-.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the relevant chemical species in the solution: Na3PO4 dissociates completely in water to form 3 Na+ ions and 1 PO4^3- ion.
Recognize that PO4^3- is a base and can accept protons from water, forming OH- ions and HPO4^2- ions. The reaction is: \( \text{PO}_4^{3-} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightleftharpoons \text{HPO}_4^{2-} + \text{OH}^- \).
Use the base dissociation constant \( K_b \) for PO4^3- to find the concentration of OH- ions. The \( K_b \) can be calculated using the relation \( K_w = K_a \times K_b \), where \( K_w \) is the ion-product constant of water and \( K_a \) is the acid dissociation constant for the conjugate acid HPO4^2-.
Set up an expression for \( K_b \) using the concentrations: \( K_b = \frac{[\text{HPO}_4^{2-}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{PO}_4^{3-}]} \). Assume \([\text{HPO}_4^{2-}] = [\text{OH}^-] = x\) and \([\text{PO}_4^{3-}] = 1 \times 10^{-3} - x\), then solve for \( x \).
Calculate the pOH from the concentration of OH- ions using \( \text{pOH} = -\log[\text{OH}^-] \), and then find the pH using \( \text{pH} = 14 - \text{pOH} \).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and pOH
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration (pH = -log[H+]). A lower pH indicates a more acidic solution, while a higher pH indicates a more basic solution. The pOH is similarly defined for hydroxide ions, and the relationship between pH and pOH is given by the equation pH + pOH = 14 at 25°C.
Recommended video:
Guided course
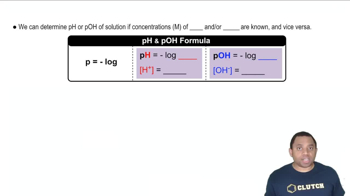
pH and pOH Calculations
Strong vs. Weak Bases
In chemistry, bases can be classified as strong or weak based on their ability to dissociate in water. Strong bases, like NaOH, completely dissociate into their ions, while weak bases only partially dissociate. Sodium phosphate (Na3PO4) is a strong base because it dissociates completely in solution, contributing to the increase in hydroxide ion concentration and thus raising the pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
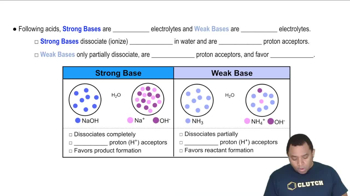
Strong vs Weak Bases
Dissociation of Sodium Phosphate
Sodium phosphate (Na3PO4) dissociates in water to produce sodium ions (Na+) and phosphate ions (PO4^3-). The phosphate ions can react with water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-), which increases the pH of the solution. Understanding this dissociation process is crucial for calculating the resulting pH of the solution, as it directly influences the concentration of hydroxide ions present.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Percent Dissociation Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Tooth enamel is composed of hydroxyapatite, whose simplest formula is Ca51PO423OH, and whose corresponding Ksp = 6.8 * 10-27. As discussed in the Chemistry and Life box on page 746, fluoride in fluorinated water or in toothpaste reacts with hydroxyapatite to form fluoroapatite, Ca51PO423F, whose Ksp = 1.0 * 10-60. (a) Write the expression for the solubility-constant for hydroxyapatite and for fluoroapatite.
Textbook Question
Calculate the solubility of Mg1OH22 in 0.50 M NH4Cl.
Textbook Question
The solubility-product constant for barium permanganate, Ba1MnO422, is 2.5 * 10-10. Assume that solid Ba1MnO422 is in equilibrium with a solution of KMnO4. What concentration of KMnO4 is required to establish a concentration of 2.0 * 10-8 M for the Ba2 + ion in solution?
Textbook Question
A solid sample of Fe1OH23 is added to 0.500 L of 0.250 Maqueous H2SO4. The solution that remains is still acidic. Itis then titrated with 0.500 M NaOH solution, and it takes12.5 mL of the NaOH solution to reach the equivalencepoint. What mass of Fe1OH23 was added to the H2SO4solution?
