Calculate the pH at the equivalence point in titrating 0.100 M solutions of each of the following with 0.080 M NaOH: (a) hydrobromic acid (HBr).
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 49
For each statement, indicate whether it is true or false. (c) The solubility of a slightly soluble salt is independent of the presence of a common ion. (d) The solubility product of a slightly soluble salt is independent of the presence of a common ion.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of solubility and solubility product (K_sp). Solubility refers to the amount of a substance that can dissolve in a solvent at a given temperature, while the solubility product is the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of a sparingly soluble salt.
Step 2: Consider the common ion effect. The common ion effect states that the solubility of a salt is reduced when one of its constituent ions is already present in the solution. This is because the presence of a common ion shifts the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier's principle.
Step 3: Analyze statement (c). The solubility of a slightly soluble salt is affected by the presence of a common ion due to the common ion effect, which decreases the solubility of the salt.
Step 4: Analyze statement (d). The solubility product (K_sp) is a constant at a given temperature and is not affected by the presence of a common ion. It only depends on the temperature and the intrinsic properties of the salt.
Step 5: Conclude the truth value of each statement based on the analysis. Statement (c) is false because solubility is affected by a common ion, while statement (d) is true because K_sp is independent of the presence of a common ion.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that applies to the solubility of sparingly soluble ionic compounds. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced equation. Ksp is specific to a particular temperature and is used to predict the solubility of salts in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Product Constant
Common Ion Effect
The common ion effect refers to the decrease in solubility of a salt when a common ion is added to the solution. This occurs because the addition of a common ion shifts the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier's principle, favoring the formation of the solid salt and reducing the concentration of dissolved ions. This effect is crucial in understanding how the presence of other ions influences solubility.
Recommended video:
Guided course
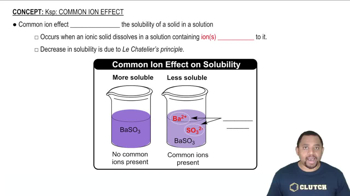
Common Ion Effect
Le Chatelier's Principle
Le Chatelier's principle states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed by changing the conditions, the system will adjust to counteract the change and restore a new equilibrium. In the context of solubility, adding a common ion shifts the equilibrium of the dissolution reaction, leading to decreased solubility of the salt. This principle is fundamental in predicting how changes in concentration affect chemical equilibria.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Le Chatelier's Principle
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point in titrating 0.100 M solutions of each of the following with 0.080 M NaOH: (b) chlorous acid (HClO2).
Textbook Question
Calculate the pH at the equivalence point in titrating 0.100 M solutions of each of the following with 0.080 M NaOH: (c) benzoic acid (C6H5COOH).
Textbook Question
The solubility of two slightly soluble salts of M2 + , MA and MZ2, is the same, 4 * 10-4 mol/L. (c) If you added an equal volume of a solution saturated in MA to one saturated in MZ2, what would be the equilibrium concentration of the cation, M2+?
1
views
Textbook Question
(a) True or false: 'solubility' and 'solubility-product constant' are the same number for a given compound.
