Lead(II) carbonate, PbCO3, is one of the components of the passivating layer that forms inside lead pipes. (d) The EPA threshold for acceptable levels of lead ions in water is 15 ppb. Does a saturated solution of lead(II) carbonate produce a solution that exceeds the EPA limit?
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 98
For each pair of compounds, use Ksp values to determine which has the greater molar solubility: (a) CdS or CuS (b) PbCO3 or BaCrO4 (c) Ni(OH)2 or NiCO3 (d) AgI or Ag2SO4.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the Ksp (solubility product constant) values for both PbCO3 and BaCrO4 from a reliable source such as a chemistry textbook or database.
Write the dissolution equations for each compound. For PbCO3, the equation is PbCO3(s) ⇌ Pb^2+(aq) + CO3^2-(aq). For BaCrO4, the equation is BaCrO4(s) ⇌ Ba^2+(aq) + CrO4^2-(aq).
Express the molar solubility (s) for each compound using the dissolution equations. For PbCO3, if s is the molar solubility, then [Pb^2+] = s and [CO3^2-] = s. For BaCrO4, [Ba^2+] = s and [CrO4^2-] = s.
Set up the Ksp expression for each compound using the concentrations derived from the molar solubility. For PbCO3, Ksp = [Pb^2+][CO3^2-] = s * s = s^2. For BaCrO4, Ksp = [Ba^2+][CrO4^2-] = s * s = s^2.
Compare the calculated s values (molar solubility) for each compound. The compound with the higher s value has the greater molar solubility.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Solubility Product Constant (Ksp)
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that quantifies the solubility of a sparingly soluble ionic compound. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the ions, each raised to the power of their coefficients in the balanced dissolution equation. A higher Ksp value indicates a greater solubility of the compound in water.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Product Constant
Molar Solubility
Molar solubility refers to the maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a given volume of solvent at equilibrium. It is typically expressed in moles per liter (M). To compare the molar solubility of two compounds, one can derive it from their Ksp values, allowing for a direct comparison of how much of each compound can dissolve in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
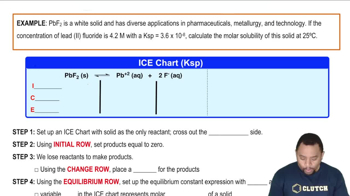
Molar Solubility Example
Dissociation of Ionic Compounds
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, they dissociate into their constituent ions. The extent of this dissociation affects the Ksp and, consequently, the molar solubility. Understanding the stoichiometry of the dissociation reaction is crucial for calculating the Ksp and determining the molar solubility of each compound, as different compounds yield different numbers of ions upon dissolution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The solubility of CaCO3 is pH dependent. (b) Use the Kb expression for the CO32- ion to determine the equilibrium constant for the reaction CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) ⇌ Ca2+(aq) + HCO3-(aq) + OH-(aq)
Textbook Question
Tooth enamel is composed of hydroxyapatite, whose simplest formula is Ca51PO423OH, and whose corresponding Ksp = 6.8 * 10-27. As discussed in the Chemistry and Life box on page 746, fluoride in fluorinated water or in toothpaste reacts with hydroxyapatite to form fluoroapatite, Ca51PO423F, whose Ksp = 1.0 * 10-60. (a) Write the expression for the solubility-constant for hydroxyapatite and for fluoroapatite.
