Textbook Question
Consider the base hydroxylamine, NH2OH. (a) What is the conjugate acid of hydroxylamine?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance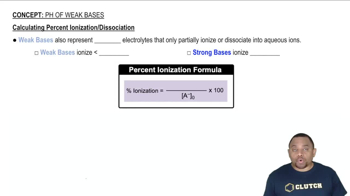

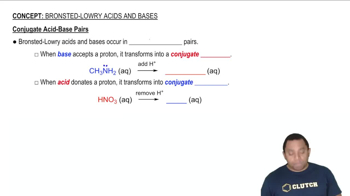
Consider the base hydroxylamine, NH2OH. (a) What is the conjugate acid of hydroxylamine?
The hypochlorite ion, ClO-, acts as a weak base. (a) Is ClO- a stronger or weaker base than hydroxylamine?
The hypochlorite ion, ClO-, acts as a weak base. (b) When ClO- acts as a base, which atom, Cl or O, acts as the proton acceptor? (c) Can you use formal charges to rationalize your answer to part (b)?
Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the reaction of each of the following bases with water: (a) propylamine, C3H7NH2
Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the reaction of each of the following bases with water: (c) benzoate ion, C6H5CO2-