Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (a) Write out the reaction that leads to this acidic pH.

Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following compounds are acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) NH4Br (b) FeCl3 (c) KClO4 (d) NaHC2O4.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Acid-Base Theory

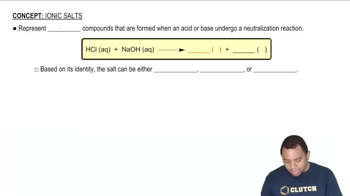
Salt Hydrolysis
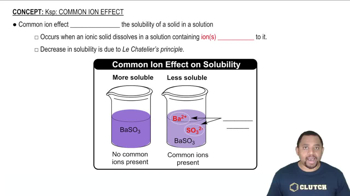
Common Ion Effect
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (b) Using Appendix D, calculate the Ka for pyridinium bromide.
Pyridinium bromide 1C5H5NHBr2 is a strong electrolyte that dissociates completely into C5H5NH+ and Br-. An aqueous solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. (c) A solution of pyridinium bromide has a pH of 2.95. What is the concentration of the pyridinium cation at equilibrium, in units of molarity?
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following compounds are acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) Na2CO3
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (a) AlCl3
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (b) NaBr
