The following diagrams represent aqueous solutions of three acids, HX, HY, and HZ. The water molecules have been omitted for clarity, and the hydrated proton is represented as H+ rather than H3O+.(b) Which acid would have the smallest aciddissociation constant, Ka?

Phenylephrine, an organic substance with molecular formula C9H13NO2, is used as a nasal decongenstant in over-thecounter medications. The molecular structure of phenylephrine is shown below using the usual shortcut organic structure. (a) Would you expect a solution of phenylephrine to be acidic, neutral, or basic?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
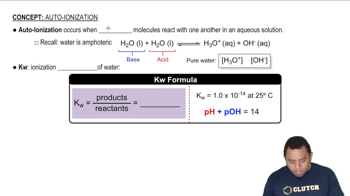
Key Concepts
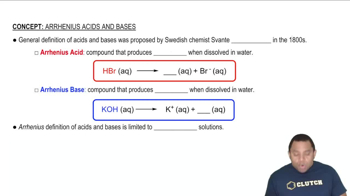
Acid-Base Chemistry
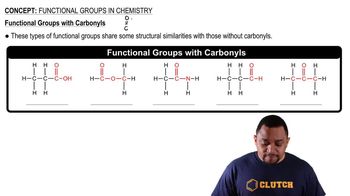
Functional Groups
Ionization of Phenylephrine
The following diagrams represent aqueous solutions of three acids, HX, HY, and HZ. The water molecules have been omitted for clarity, and the hydrated proton is represented as H+ rather than H3O+.(c) Which solution would have the highest pH?
Each of the three molecules shown here contains an OH group, but one molecule acts as a base, one as an acid, and the third is neither acid nor base. (c) Which one is neither acidic nor basic?
Phenylephrine, an organic substance with molecular formula C9H13NO2, is used as a nasal decongenstant in over-thecounter medications. The molecular structure of phenylephrine is shown below using the usual shortcut organic structure. (c) Would you expect a solution of phenylephrine hydrochloride to be acidic, neutral, or basic?
Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (a) If X is the same atom in both molecules, which molecule will be more acidic?
Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (b) Does the acidity of each molecule increase or decrease as the electronegativity of the atom X increases?
