Each of the three molecules shown here contains an OH group, but one molecule acts as a base, one as an acid, and the third is neither acid nor base. (c) Which one is neither acidic nor basic?

Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (a) If X is the same atom in both molecules, which molecule will be more acidic?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
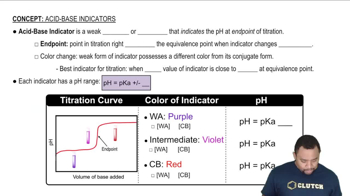
Acidity and pKa
Inductive Effect
Resonance Stabilization

Phenylephrine, an organic substance with molecular formula C9H13NO2, is used as a nasal decongenstant in over-thecounter medications. The molecular structure of phenylephrine is shown below using the usual shortcut organic structure. (a) Would you expect a solution of phenylephrine to be acidic, neutral, or basic?
Phenylephrine, an organic substance with molecular formula C9H13NO2, is used as a nasal decongenstant in over-thecounter medications. The molecular structure of phenylephrine is shown below using the usual shortcut organic structure. (c) Would you expect a solution of phenylephrine hydrochloride to be acidic, neutral, or basic?
Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (b) Does the acidity of each molecule increase or decrease as the electronegativity of the atom X increases?
NH31g2 and HCl(g) react to form the ionic solid NH4Cl1s2. Which substance is the Brønsted–Lowry acid in this reaction? Which is the Brønsted–Lowry base?
