Phenylephrine, an organic substance with molecular formula C9H13NO2, is used as a nasal decongenstant in over-thecounter medications. The molecular structure of phenylephrine is shown below using the usual shortcut organic structure. (c) Would you expect a solution of phenylephrine hydrochloride to be acidic, neutral, or basic?

For each of these reactions, identify the acid and base among the reactants, and state if the acids and bases are Lewis, Arrhenius, and/or Brønsted–Lowry: (a) PCl4^+ + Cl^- → PCl5 (b) NH3 + BF3 → H3NBF3 (c) [Al(H2O)6]^3+ + H2O → [Al(H2O)5OH]^2+ + H3O^+
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Acid-Base Theories

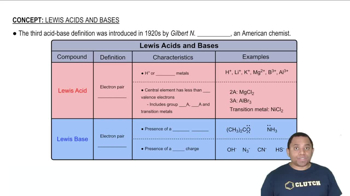
Lewis Acids and Bases
Proton Transfer Reactions

Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (a) If X is the same atom in both molecules, which molecule will be more acidic?
Consider the molecular models shown here, where X represents a halogen atom. (b) Does the acidity of each molecule increase or decrease as the electronegativity of the atom X increases?
NH31g2 and HCl(g) react to form the ionic solid NH4Cl1s2. Which substance is the Brønsted–Lowry acid in this reaction? Which is the Brønsted–Lowry base?
Which of the following statements is false? (a) An Arrhenius base increases the concentration of OH- in water. (b) A Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. (c) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry acid. (d) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry base. (e) Any compound that contains an –OH group acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base.
Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HIO3, (ii) NH4+.
