Predict the stronger acid in each pair: (c) HBrO3 or HBrO2

Based on their compositions and structures and on conjugate acid–base relationships, select the stronger base in each of the following pairs: (a) BrO- or ClO- (c) HPO42- or H2PO4-
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
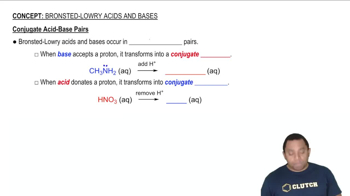
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Electronegativity and Stability

Acid-Base Strength Trends

Predict the stronger acid in each pair: (e) benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) or phenol (C6H5OH).
Based on their compositions and structures and on conjugate acid–base relationships, select the stronger base in each of the following pairs: (b) BrO- or BrO2-
Based on their compositions and structures and on conjugate acid–base relationships, select the stronger base in each of the following pairs: (b) PO43- or AsO43-
Indicate whether each of the following statements is true or false. For each statement that is false, correct the statement to make it true. (a) In general, the acidity of binary acids increases from left to right in a given row of the periodic table. (b) In a series of acids that have the same central atom, acid strength increases with the number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the central atom. (c) Hydrotelluric acid 1H2Te2 is a stronger acid than H2S because Te is more electronegative than S.
