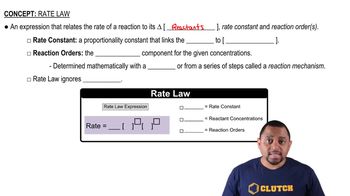
Consider the following reaction between mercury(II) chloride and oxalate ion:
2 HgCl2(aq) + C2O42-(aq) → 2 Cl-(aq) + 2 CO2(g) + Hg2Cl2(s)
The initial rate of this reaction was determined for several concentrations of HgCl2 and C2O42-, and the following rate data were obtained for the rate of disappearance of C2O42-:
Experiment [HgCl2] (M) [C2O42-] (M) Rate (M/s)
1 0.164 0.15 3.2 × 10-5
2 0.164 0.45 2.9 × 10-4
3 0.082 0.45 1.4 × 10-4
4 0.246 0.15 4.8 × 10-5
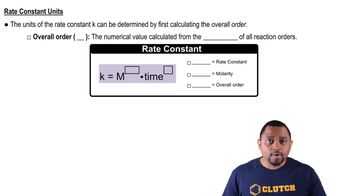
(b) What is the value of the rate constant with proper units?
(c) What is the reaction rate when the initial concentration of HgCl2 is 0.100 M and that of C2O42- is 0.25 M if the temperature is the same as that used to obtain the data shown?