Textbook Question
The addition of NO accelerates the decomposition of N2O, possibly by the following mechanism: NO1g2 + N2O1g2¡N21g2 + NO21g2 2 NO21g2¡2 NO1g2 + O21g2 (b) Is NO serving as a catalyst or an intermediate in this reaction?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance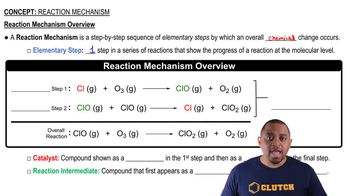

The addition of NO accelerates the decomposition of N2O, possibly by the following mechanism: NO1g2 + N2O1g2¡N21g2 + NO21g2 2 NO21g2¡2 NO1g2 + O21g2 (b) Is NO serving as a catalyst or an intermediate in this reaction?
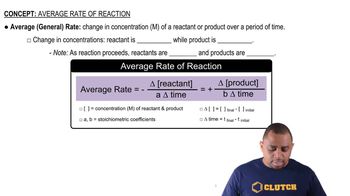
Many metallic catalysts, particularly the precious-metal ones, are often deposited as very thin films on a substance of high surface area per unit mass, such as alumina (Al2O3) or silica (SiO2). (b) How does the surface area affect the rate of reaction?