The density of acetonitrile (CH3CN) is 0.786 g/mL and the density of methanol (CH3OH) is 0.791 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 22.5 mL of CH3OH in 98.7 mL of CH3CN. (c) Assuming that the volumes are additive, what is the molarity of CH3OH in the solution?

Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (a) 600 mL of 0.250 M SrBr2,
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
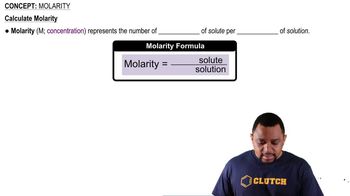
Molarity (M)
Volume Conversion

Calculating Moles from Molarity

The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (a) Calculate the mole fraction of thiophene in the solution.
The density of toluene (C7H8) is 0.867 g/mL, and the density of thiophene (C4H4S) is 1.065 g/mL. A solution is made by dissolving 8.10 g of thiophene in 250.0 mL of toluene. (b) Calculate the molality of thiophene in the solution.
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (b) 86.4 g of 0.180 m KCl,
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following aqueous solutions: (c) 124.0 g of a solution that is 6.45% glucose (C6H12O6) by mass.
Calculate the number of moles of solute present in each of the following solutions: (a) 255 mL of 1.50 M HNO3(aq),
