State whether each sentence is true or false: (b) Metals have high electrical conductivities because they are denser than other solids.

The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (e) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Molecular Orbitals
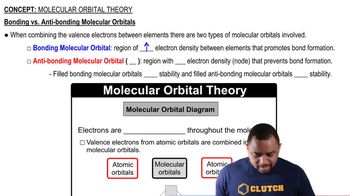
Nodes in Molecular Orbitals

Linear Chains of Atoms

The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (a) How many molecular orbitals are there in the diagram?
The molecular-orbital diagrams for two- and four-atom linear chains of lithium atoms are shown in Figure 12.22. Construct a molecular-orbital diagram for a chain containing six lithium atoms and use it to answer the following questions: (c) How many nodes are in the highest-energy molecular orbital?
Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (b) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy molecular orbital? (c) How many nodes are in the highestenergy molecular orbital? (d) How many nodes are in the highest-energy occupied molecular orbital (HOMO)? (e) How many nodes are in the lowest-energy unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)?
Repeat Exercise 12.51 for a linear chain of eight lithium atoms. (f) How does the HOMO–LUMO energy gap for this case compare to that of the four-atom case?
Which would you expect to be the more ductile element, (a) Ag or Mo? (b) Zn or Si? In each case explain your reasoning.
