Which statement correctly describes a difference between graphene and graphite? (a) Graphene is a molecule but graphite is not. (b) Graphene is a single sheet of carbon atoms and graphite contains many, and larger, sheets of carbon atoms. (c) Graphene is an insulator but graphite is a metal. (d) Graphite is pure carbon but graphene is not. (e) The carbons are sp2 hybridized in graphene but sp3 hybridized in graphite.
Ch.12 - Solids and Modern Materials

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 12, Problem 103a
Selected chlorides have the following melting points: NaCl (801 °C), MgCl2 (714 °C), PCl3 (-94 °C), SCl2 (-121 °C) (a) For each compound, indicate what type its solid form is (molecular, metallic, ionic, or covalent-network).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the type of bonding present in each compound based on the elements involved.
NaCl is composed of a metal (Na) and a non-metal (Cl), indicating it is an ionic compound.
MgCl2 is also composed of a metal (Mg) and a non-metal (Cl), indicating it is an ionic compound.
PCl3 consists of non-metals (P and Cl), suggesting it is a molecular compound with covalent bonds.
SCl2 consists of non-metals (S and Cl), suggesting it is a molecular compound with covalent bonds.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed from the electrostatic attraction between positively and negatively charged ions. They typically consist of a metal and a non-metal, resulting in a crystalline structure that exhibits high melting points due to strong ionic bonds. Examples include NaCl and MgCl2, which are solid at room temperature and have high melting points.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionic Compounds Naming
Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are formed when two or more non-metals share electrons through covalent bonds. These compounds usually have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds and can exist as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature. PCl3 and SCl2 are examples of molecular compounds, characterized by their discrete molecular units.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Naming Molecular Compounds
Melting Points and Bonding Types
The melting point of a substance is influenced by the type of bonding present. Ionic compounds generally have high melting points due to the strong forces between ions, while molecular compounds have lower melting points due to weaker van der Waals forces. Understanding the relationship between bonding types and melting points helps in classifying compounds accurately.
Recommended video:
Guided course
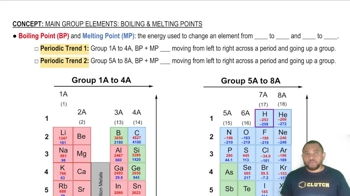
Boiling Point and Melting Point
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Imagine the primitive cubic lattice. Now imagine pushing on top of it, straight down. Next, stretch another face by pulling it to the right. All angles remain 90°. What kind of primitive lattice have you made?
Textbook Question
Pure iron crystallizes in a body-centered cubic structure, shown in the figure. but small amounts of impurities can stabilize a facecentered cubic structure. Which form of iron has a higher density?
