Textbook Question
Write the chemical equation that represents the formation of (b) polyacrylonitrile from acrylonitrile (polyacrylonitrile is used in home furnishings, craft yarns, clothing, and many other items).

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance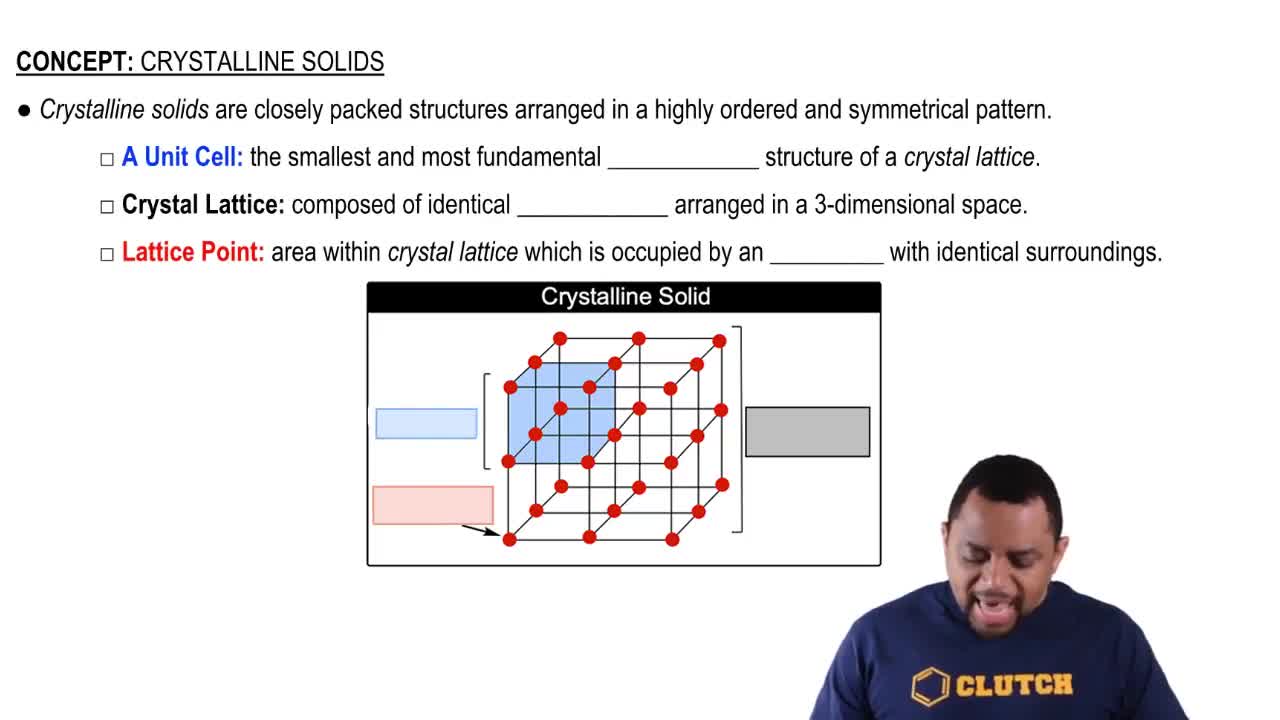

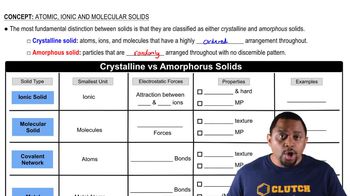
Write the chemical equation that represents the formation of (b) polyacrylonitrile from acrylonitrile (polyacrylonitrile is used in home furnishings, craft yarns, clothing, and many other items).
What molecular structural features cause high-density polyethylene to be denser than low-density polyethylene?
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) Elastomers are rubbery solids. (b) Thermosets cannot be reshaped. (c) Thermoplastic polymers can be recycled.
CdS has a band gap of 2.4 eV. If large crystals of CdS are illuminated with ultraviolet light, they emit light equal to the band gap energy. (a) What color is the emitted light?