Textbook Question
Which would you expect to be the more ductile element, (a) Ag or Mo? (b) Zn or Si? In each case explain your reasoning.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Which would you expect to be the more ductile element, (a) Ag or Mo? (b) Zn or Si? In each case explain your reasoning.
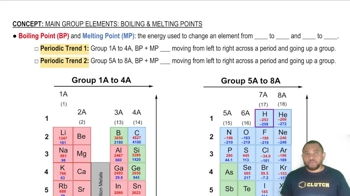
Which of the following statements does not follow from the fact that the alkali metals have relatively weak metal–metal bonding? (a) The alkali metals are less dense than other metals. (b) The alkali metals are soft enough to be cut with a knife. (c) The alkali metals are more reactive than other metals. (d) The alkali metals have higher melting points than other metals. (e) The alkali metals have low ionization energies.
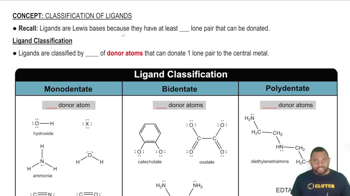
Tausonite, a mineral composed of Sr, O, and Ti, has the cubic unit cell shown in the drawing. (a) What is the empirical formula of this mineral?